Electrolyte Disorders
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Hyperkalemia
ECG characteristics of hyperkalemia, high blood potassium:
- P-waves are widened and of low amplitude due to slowing of conduction
- QRS complex:
- QRS widening
- fusion of QRS-T
- loss of the ST segment
- Tall tented T waves
The initial part of the QRS complex is often spared as purkinje fibers are less sensitive to hyperkalemia. These changes can also occur in acidosis (via the same mechanism) and during Class IC anti-arrhythmic intoxication.
At concentrations > 7.5 mmol/L atrial and ventricular fibrillation can occur.
-
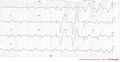
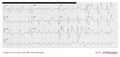
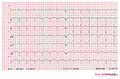
Consecutive ECGs of a patient with hyperkalemia. ECG1
-
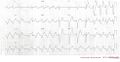
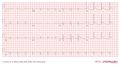
Consecutive ECGs of a patient with hyperkalemia. ECG2
-
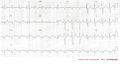
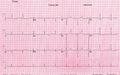
Consecutive ECGs of a patient with hyperkalemia. After correction of potassium levels. ECG3
-
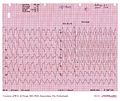
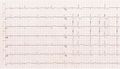
Another patient, potassium of 9.4 mmol/L
-
Potassium 7.5 mmol/L. More ECGs
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia, low blood potassium, results in:
- ST depression and flattening of the T wave
- Negative T waves
- A U-wave may be visible
-
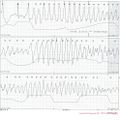
A patient with hypokalemia, prominent QT prolongation. Not the extrasystoles originating from the prolonged T/U wave. This patient definitely needs rhythm monitoring
-
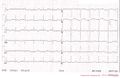
patient A
-
patient A
-
patient B
-
Patient C, Potassiumlevel of 1.5
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, high blood calcium, speeds repolarization. Characteristics of hypercalcemia:
- Mild: broad based tall peaking T waves
- Severe: extremely wide QRS, low R wave, disappearance of p waves, tall peaking T waves.
-
A patient with severe hypercalcemia: Calcium 4.6 mmol/L, albumin 37 g/L
Hypocalcemia
ECG-characteristics of hypocalcemia, low blood calcium:
- Narrowing of the QRS complex
- Reduced PR interval
- T wave flattening and inversion
- Prolongation of the QT-interval
- Prominent U-wave
- Prolonged ST and ST-depression
-
An ECG of a patient with hypocalcemia