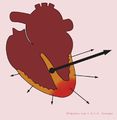
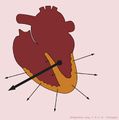
QRS axis
| «Step 3: Conduction (PQ, QRS, QT, QTc) | Step 5: P wave morphology» |
| Author(s) | I.A.C. van der Bilt, MD | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
How do you determine the electrical heartaxis


<flashow>http://nl.ecgpedia.org/images/b/bc/Normal_SR_vector.swf%7Cheight=300px</flashow> When you average all electrical signals from the heart, you can indicate the direction of the average electrical depolarization with an arrow (vector). This is the heartaxis. Especially a change of the heartaxis or an extreme deviation can be an indication for pathology.
- Largest QRS deflection in lead I: the electrical activity is directed to the left (of the patient)
- Largest QRS deflection in lead AVF: the electrical activity is directed down.
This indicates a normal heartaxis. Usually, these two leads are enough to diagnose a normal heartaxis!
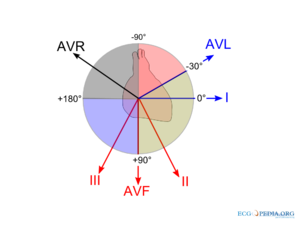
The largest vector in the heart is from the AV-node in the direction of the ventricular depolarization. Under normal circumstances, this is directed left and down.(towards leads I and AVF). The position of the QRS vector is given in degrees. See the figure, the middle of the figure is the AV-node. A horizontal line towards the left arm is defined as 0 degrees.
A normal heartaxis is between -30 and +90 degrees.
Rule: biggest QRS deflection in I and II is an intermediate = normal heartaxis. So positive deflections in I and II indicates a normal heartaxis.
Interpretation
The interpretation of the electrical heartaxis has a few rules of thumb:
- First, when a positive depolarization wave moves towards a positive electrode, a positive, upwards deflection is registered on the ECG.
- Second, there are 4 quadrants where the QRS-vector can point to:
- left upper quadrant --> left axis deviation (between -30º and -90º)
- left lower quadrant --> normal (between -30º and 90º)
- right below and right --> right axis deviation (between 90º and -150º)
- right upper quadrant --> extreme axis (between -90º and -150º)
Example:
The QRS in lead I, will have a negative deflection in a right axis deviation. The vector is not directed towards the electrode. However, lead AVF will be positive, the vector is directed towards the electrode.
- Iso-electrical
- When the depolarization is perpendicular on the lead, this is called iso-electrical. The QRS is neither positive nor negative.
- Undetermined axis
- When all extremity leads are biphasic, the axis is directed to the front or back, in a transverse plane. The axis is than undetermined.
Abnormal heartaxis
-
Heartaxis deviation to the left in case of an inferior infarct. Left anterior hemi Block is a common cause. A left axis is between -30 and -90 degrees. The axis is -30 degrees.
-
Heartaxis deviation to the right in right ventricular load, as in COPD or pulmonary embolism. A right axis is between +90 and +180 degrees. In this case the axis is +135 degrees
The direction of the vector can changes under different circumstances:
- When the heart itself is rotated (right ventricular overload), obviously the axis turns with it.
- In case of ventricular hypertrophy, the axis will deviate by the bigger electrical activity and the vector will turn towards the hypertrophied tissue.
- Infarcted tissue is electrically dead. No electrical activity is registered and the QRS vector turns away from the infarcted tissue
- In conduction problems, the axis deviates too. When the right ventricle depolarizes later than the left ventricle, the axis will turn to the right (RBBB). This is because the right ventricle will begin the contraction later and therefore will also finish later. In a normal situation the vector is influenced by the left ventricle but now only by the right ventricle.
Left axis deviation

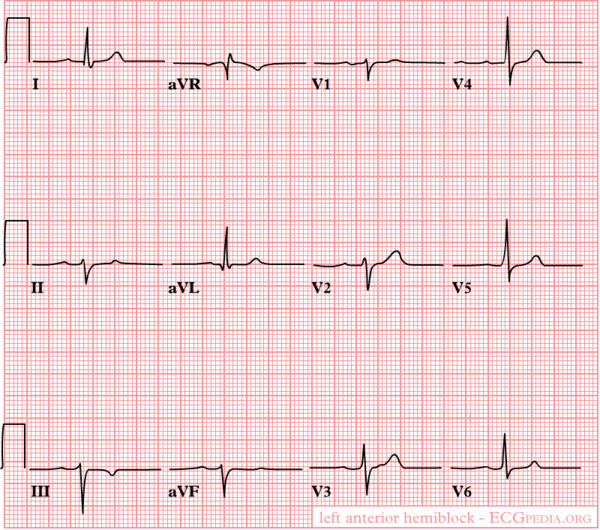
Causes of left axis deviation include:
- Normal variation (physiologic, often with age)
- Mechanical shifts, such as expiration, high diaphragm (pregnancy, ascites, abdominal tumor)
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Left bundle branch block
- left anterior fascicular block
- Congenital heart disease (e.g. atrial septal defect)
- Emphysema
- Hyperkalemia
- Ventricular ectopic rhythms
- Preexcitation syndromes
- Inferior myocardial infarction
- Pacemaker rhythm
Right axis deviation
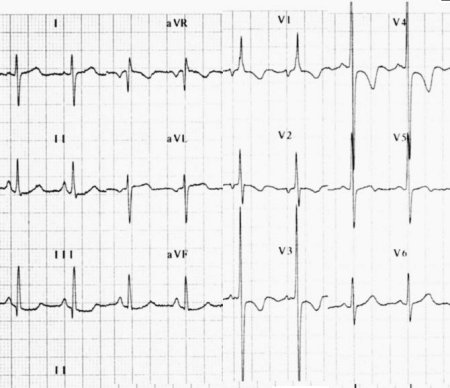
Causes of right axis deviation include:
- Normal variation (vertical heart with an axis of 90º)
- Mechanical shifts, such as inspiration and emphysema
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Right bundle branch block
- Left posterior fascicular block
- Dextrocardia
- Ventricular ectopic rhythms
- Preexcitation syndromes
- Lateral wall myocardial infarction
- Right ventricular load, for example Pulmonary Embolism or Cor Pulmonale (as in COPD)