Approach to the Wide Complex Tachycardia: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{| class="wikitable" width="500px" | {| class="wikitable" width="500px" | ||
! colspan="3" | Morphological criteria (if the above criteria are inconclusive) | ! colspan="3" | Morphological criteria (if the above criteria are inconclusive) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 46: | Line 36: | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
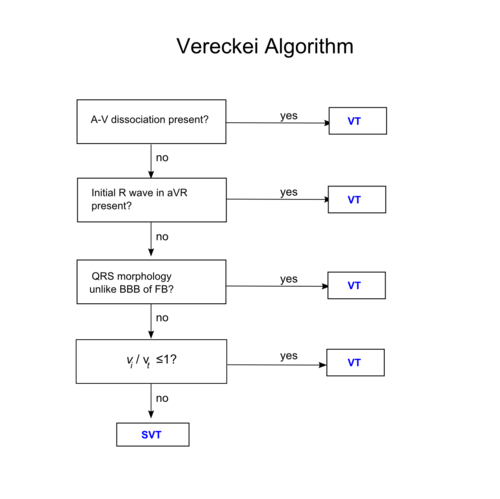
== Vereckei algorithm <cite>Vereckei</cite>== | == Vereckei algorithm <cite>Vereckei</cite>== | ||
[[File:Vereckei_algorithm.png|500px|thumb|left]] | [[File:Vereckei_algorithm.png|500px|thumb|left]] | ||
Revision as of 21:33, 12 November 2009
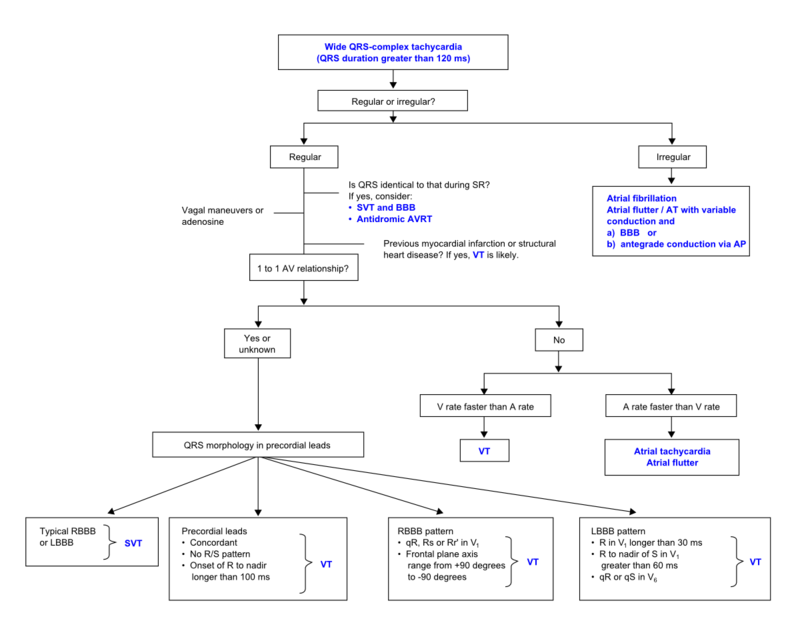
During wide complex tachycardia (heart rate > 100/min, QRS > 0.12 sec) the differentiation between supraventricular and ventricular origin of the arrhythmia is important to guide therapy. Several algorhythms have been developed to aid in this differentiation (below). It is important to keep in mind that a good estimate of VT versus SVT can be made based on the clinical vignette:
- 'Horizontal entrance' into the ER. Older patient with previous myocardial infarction = most likely VT
- Younger patient with known paroxysmal tachycardias and who is hemodynamically stable = most like SVT
The ACC algorhythm ACC
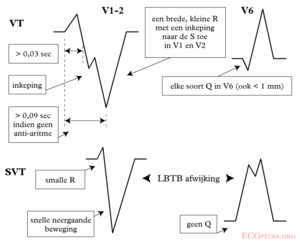
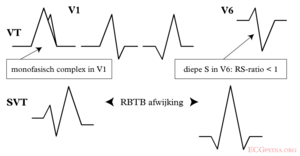
Brugada criteria
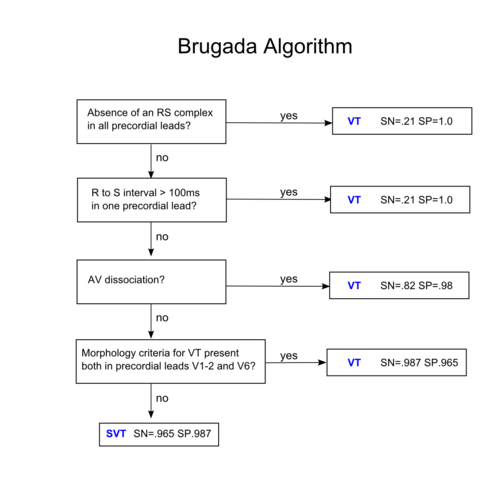
| Morphological criteria (if the above criteria are inconclusive) | ||
|---|---|---|
| LBBB pattern | ||
| Initial R more than 40ms? | Yes => VT | 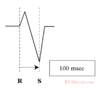 |
| Slurred or notched downwards leg of S wave in leads V1 or V2 | Yes => VT | |
| Beginning of Q to nadir QS >60 ms in V1 or V2? | Yes => VT | LR >50:1 |
| Q or QS in V6? | Yes => VT | LR >50:1 |
 | ||
| RBBB pattern | ||
| Monofasic R or qR in V1? | Yes => VT | |
| R taller than R' (rabbit-ear sign)? | Yes => VT | LR >50:1 |
| rS in V6? | Yes => VT | LR >50:1 |
 | ||
Vereckei algorithm Vereckei
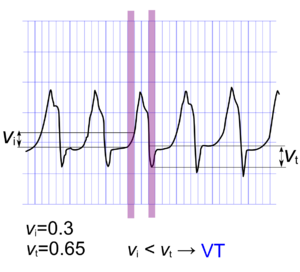
Examples
-
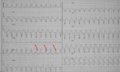
Wide complex tachycardia. No AV dissociation. RBBB. Resembles sinus rhythm from the same patient. Conclusio SVT with RBBB
-
ECG from the same patient in sinus rhythm. The QRS complex is very similiar.
-
Wide complex tachycardia. LBBB configuration. Absence of RS in the chest leads. AV dissociation is present. Conclusion: VT
-
Wide complex tachycardia. LBBB configuration. Absence of RS in the chest leads. AV dissociation is present. Conclusion: VT
Referenties
<biblio>
- ACC pmid=14563598
- Brug1 pmid=2022022
- Vereckei pmid=17272358
</biblio>