Clinical Disorders: Difference between revisions
| (30 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Medication== | ==Medication== | ||
===Digoxin=== | ===Digoxin=== | ||
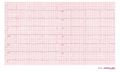
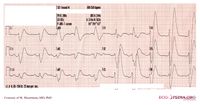
[[Image:med_digitalis.png|thumb|300px|Typical for digoxin intoxication is the | [[Image:med_digitalis.png|thumb|300px|Typical for digoxin intoxication is the oddly shaped ST-depression]] | ||
ECG changes typical for digoxin | ECG changes typical for digoxin '''use''' (digoxin = Lanoxin) are: | ||
* | *Oddly shaped ST-depression with 'scooped out' appearance of the ST segment (see figure) | ||
* | *Flat, negative or biphasic T wave | ||
*Short QT interval | *Short QT interval | ||
*Increased u-wave amplitude | *Increased u-wave amplitude | ||
*Prolonged PR-interval | *Prolonged PR-interval | ||
* | *Sinus bradycardia | ||
* | ECG changes typical for digoxin '''intoxication''' are: | ||
*Bradyarrhythmias: | |||
**AV block. Including complete AV block and Wenkebach. | **AV block. Including complete AV block and Wenkebach. | ||
*Tachyarrhythmias: | *Tachyarrhythmias: | ||
**Junctional tachycardia | **Junctional tachycardia | ||
** | **Atrial tachycardia | ||
**Ventricular ectopia, bigemini, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia | **Ventricular ectopia, bigemini, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia | ||
Intoxication can lead to | Intoxication can lead to an SA-block or AV-block, sometimes in combination with tachycardia. '''NB''' these effects are increased by hypokalemia. In extreme high concentrations rhythm disturbances (''ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation'') may develop. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=== | |||
* ''' | ===Antiarrhythmics=== | ||
** | * '''Anti-arrhythmics:''' These may lead to several ECG-changes; | ||
** | **Broad and irregular P-wave | ||
** | **Broad QRS complex | ||
** | **Prolonged QT interval (brady-, tachycardia, AV-block, ventricular tachycardia) | ||
**Prominent U-wave | |||
**In case of intoxication, the above mentioned characteristics are more prominent | **In case of intoxication, the above mentioned characteristics are more prominent | ||
Additionally, several | Additionally, several arrhthytmias can be seen. | ||
===Beta blockers=== | |||
[[File:E000542.jpg|thumb|right|ECG of a patient with atenolol intoxication]]Beta blocker intoxication can result in bradycardia, hypotension, QRS widening and seizures. In a series of 260 patients with beta blocker intoxication, 41 (15%) developed cardiovascular morbidity and 4 (1.4%) died. Cardioactive coingestant (e.g. calcium channel blockers) was the only factor significantly associated with the development of cardiovascular morbidity. <cite>bb</cite> | |||
{{clr}} | |||
=== Nortriptyline | === Nortriptyline Intoxication === | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
{| | {| | ||
| | | | ||
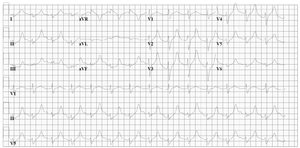
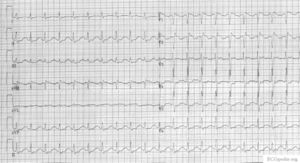
[[Image:ECG_nortr_intox.png|thumb|left|300px|An example of severe nortriptyline intoxication. The inhibitory effect | [[Image:ECG_nortr_intox.png|thumb|left|300px|An example of severe nortriptyline intoxication. The inhibitory effect on the sodium channel manifests as a broadened QRS complex and a prolonged QT interval.]] | ||
| | | | ||
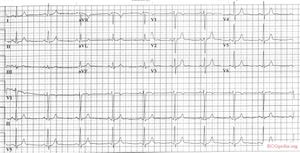
[[Image:ECG_TCA_intox.jpg|thumb|left|300px| Another example of severe nortriptyline intoxication.]] | [[Image:ECG_TCA_intox.jpg|thumb|left|300px| Another example of severe nortriptyline intoxication.]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 49: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
=== Amitriptyline | === Amitriptyline Intoxication === | ||
<div align="center"> | <div align="center"> | ||
{| | {| | ||
| | | | ||
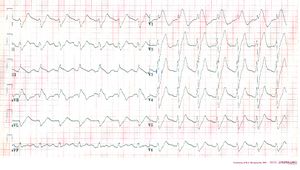
[[Image:ECG_amitr_OD_during.jpg|thumb|300px| An example of a severe | [[Image:ECG_amitr_OD_during.jpg|thumb|300px| An example of a severe amitriptyline intoxication. The inhibitory effect on the sodium channel manifests as a broadened QRS complex.]] | ||
| | | | ||
[[Image:ECG_amitr_OD_before.jpg|thumb|300px| An ECG of the same patient before the intoxication.]] | [[Image:ECG_amitr_OD_before.jpg|thumb|300px| An ECG of the same patient before the intoxication.]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 64: | ||
==Myocarditis== | ==Myocarditis== | ||
[[File:E000535.jpg|thumb|A patient with myocarditis and pericarditis showing diffuse ST elevation]] | |||
[[w:Myocarditis|Myocarditis]] is an inflammation of the myocardium and the interstitium. The symptoms are faint chest pain, abnormal heart rate and progressive heart failure. It can be caused by several factors: viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, spirochetes, auto-immune reactions, borreliosis (Lyme's disease) and HIV/AIDS. | |||
Acute peri/myocarditis causes nonspecific ST segment changes. These can be accompanied by supraventricular and ventricular rhythm disturbances and T-wave abnormalities. | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Pulmonary Embolism== | |||
==Pulmonary | |||
See the chapter [[Pulmonary Embolism]] | See the chapter [[Pulmonary Embolism]] | ||
==Chronic | ==Chronic Pulmonary Disease Pattern== | ||
The ECG shows low | [[File:E000004.jpg|thumb|right|An example of right ventricular hypertrophy (and right atrial enlargement) in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation.]]The ECG shows low voltage QRS complexes in leads I, II, and III and a right axis deviation. This is caused by the increased pressure on the right chamber. This leads to right ventricular hypertrophy. | ||
{{clr}} | |||
==Pacemaker== | ==Pacemaker== | ||
| Line 74: | Line 81: | ||
==Tamponade== | ==Tamponade== | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:ECG000028.jpg|thumb|Electrical alternans on the ECG]] | ||
In case of | In case of tamponade, fluid collects in the pericardium. Because the pericardium is stiff, the heart is compressed, resulting in filling difficulties. This is a potentially life-threatening situation and should be treated with pericardiocentesis, drainage of the fluid. Tamponade can be the result of pericarditis or myocarditis. After a myocardial infarction a tamponade can also develop; this is called Dresslers' Syndrome. In case of cancer,increased pericardial fluid may develop. This is usually caused by pericarditis carcinomatosis, meaning that the cancer has spread to the pericardium | ||
The ECG shows: | The ECG shows: | ||
*Sinus tachycardia | *Sinus tachycardia | ||
*Low- | *Low-voltage QRS complexes [[microvoltages]] | ||
*Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias | *Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias | ||
*PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an [[Ischemia#Atriaal_.2F_boezem_infarct|atrial infarction]]) | *PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an [[Ischemia#Atriaal_.2F_boezem_infarct|atrial infarction]]) | ||
| Line 85: | Line 92: | ||
==Ventricular Aneurysm== | ==Ventricular Aneurysm== | ||
The ECG pattern suggests an acute MI. All classical signs of MI may occur:; Q | The ECG pattern suggests an acute MI. All classical signs of MI may occur:; Q waves, ST segment elevations (>1mm, >4 weeks present)and T wave inversions are present. To exclude an acute MI, comparison with old ECG's is compulsory (MI has occurred years before). | ||
==Dilated Cardiomyopathy== | ==Dilated Cardiomyopathy== | ||
Often, a LBBB or broadened QRS-complex can be seen. Additionally, | Often, a LBBB or broadened QRS-complex can be seen. Additionally, nonspecific ST segment changes are present with signs of left atrial enlargement. | ||
==Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy== | ==Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy== | ||
A HOCM is | A HOCM is a hereditary illness. | ||
On the ECG there are signs of [[hypertrophy|left ventricular hypertrophy]] and [[P wave morphology|left atrial enlargement]]. | On the ECG there are signs of [[hypertrophy|left ventricular hypertrophy]] and [[P wave morphology|left atrial enlargement]]. | ||
==Electrolyte | ==Electrolyte Disturbances== | ||
See chapter: [[electrolyte disturbances]] | See chapter: [[electrolyte disturbances]] | ||
==Hypothermia== | ==Hypothermia== | ||
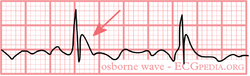
[[Image:osborne.png|thumb|left|250px| An | [[Image:osborne.png|thumb|left|250px| An Osborn J wave]] | ||
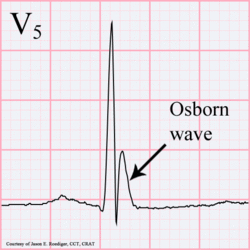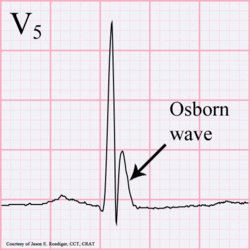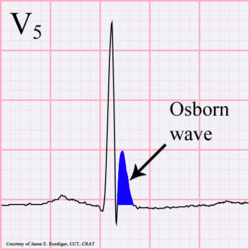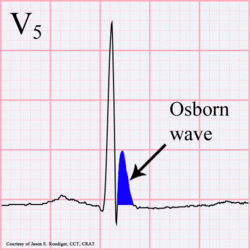
[[Image:Osborn-wave.gif|thumb|left|250px|Osborn wave. 81-year-old black male with BP 80/62 and temperature 89.5 degrees F (31.94 C).]] | |||
<div style="float:right"> | <div style="float:right"> | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:osborne_ecg.jpg|A 12 lead ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 32 degrees Celsius. Note the | Image:osborne_ecg.jpg|A 12 lead ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 32 degrees Celsius. Note the sinus bradycardia, the prolonged QT interval (QTc is not prolonged) and the Osborn J wave, most prominently in leads V2-V5 | ||
Image:JJ0001.jpg|An ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 28 degrees Celsius. | Image:JJ0001.jpg|An ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 28 degrees Celsius. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
In hypothermia a number of specific changes can be seen;<cite>hypoth</cite> | In hypothermia a number of specific changes can be seen;<cite>hypoth</cite> | ||
* | * Sinus bradycardia | ||
* | * Prolonged QTc-interval | ||
* ST | * ST segment elevation (inferior and left precordial leads) | ||
* | * Osborn-waves (slow deflections at the end of the QRS-complex) | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
==ECG | ==ECG Changes after Neurologic Events== | ||
[[Image:ECG_SAB.png|thumb| ECG of a 74 year old patient with a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Note the negative T-waves and the prolonged QT interval.]] | [[Image:ECG_SAB.png|thumb| ECG of a 74 year old patient with a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Note the negative T-waves and the prolonged QT interval.]] | ||
In 1938, Aschenbrenner <cite>Aschenbrenner</cite> noted that | In 1938, Aschenbrenner <cite>Aschenbrenner</cite> noted that repolarization abnormalities may occur after increased intracranial pressure. Since then, many publications have described ECG changes after acute neurological events. | ||
ECG changes that may occur are: | |||
* | *Q waves | ||
*ST | *ST segment elevations, | ||
*ST | *ST segment depressions, | ||
*T | *T wave changes. Large negative T waves over the precordial leads are observed frequently. | ||
* | *Prolonged QT-interval. | ||
* | *Prominent u-waves. | ||
These | These abnormalities are frequently seen after [[w:Subarachnoid_hemorrhage|subarachnoid_hemorrhage (SAH)]] (if measured serially, almost every SAH patients has at least one abnormal ECG.), but also in [[w:Subdural_hematoma|subdural hematoma]], ischemic [[w:Cerebrovascular_accident|CVA]]'s, [[w:Brain_tumor|brain Tumors]], [[w:Guillain-Barre|Guillain Barré]], [[w:Epilepsy|epilepsy]] and [[w:Migraine|migraine]]. The ECG changes are generally reversible and have limited prognostic value. However, the ECG changes can be accompanied with myocardial damage and echocardiographic changes. The cause of the ECG changes is not yet clear. The most common hypothesis is that of a neurotramitter "catecholamine storm" caused by sympathetic stimulation. | ||
==Cardiac | ==Cardiac Contusion== | ||
Cardiac contusion (in latin: contusio cordis or commotio cordis) is caused by a blunt trauma to the chest, often caused by a car | Cardiac contusion (in latin: contusio cordis or commotio cordis) is caused by a blunt trauma to the chest, often caused by a car or motorbike accident or in martial arts<cite>Maron</cite>. Rhythm disturbances and even heart failure can occur. Diagnosis is made using echocardiography and laboratory testing for cardiac enzymes. | ||
Possible ECG changes are:<cite>Sybrandy</cite> | Possible ECG changes are:<cite>Sybrandy</cite> | ||
''' | '''Nonspecific changes''' | ||
*Pericarditis-like ST elevation or PTa depression | *Pericarditis-like ST elevation or PTa depression | ||
*Prolonged QT interval | *Prolonged QT interval | ||
| Line 138: | Line 146: | ||
*ST-T segment elevation or depression | *ST-T segment elevation or depression | ||
'''Conduction delay''' | '''Conduction delay''' | ||
*Right | *Right bundle branch block | ||
*Fascicular blok | *Fascicular blok | ||
*AV delay(1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree AV blok) | *AV delay(1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree AV blok) | ||
'''Arrhythmias''' | '''Arrhythmias''' | ||
* | *Sinus tachycardia | ||
*Atrial and ventricular extrasystoles | *Atrial and ventricular extrasystoles | ||
*Atrial fibrillation | *Atrial fibrillation | ||
*Ventricular tachycardia | *Ventricular tachycardia | ||
*[[Arrhythmias#Ventricular fibrillation|Ventricular fibrillation]] | *[[Arrhythmias#Ventricular fibrillation|Ventricular fibrillation]] | ||
* | *Sinus bradycardia | ||
* | *Atrial tachycardia | ||
==Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome== | ==Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome== | ||
The Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome is a pre-excitation syndrome in which the atria are connected to the lower part of the AV node or bundle of His. On the ECG: | The Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome is a pre-excitation syndrome in which the atria are connected to the lower part of the AV node or bundle of His. On the ECG: | ||
* | * Short PR interval, < 120 ms | ||
* | * Normal QRS complex | ||
* | * No delta wave | ||
==Left and right | ==Ebstein== | ||
[[File:E000403.jpg|thumb|300px|ECG from a patient with Ebstein's anomaly showing huge P waves and low amplitude QRS waves. RBBB and T wave inversion are not present on this ECG.]] | |||
In Ebstein anomaly the tricuspid valve is inserted more apically than normal. This yields a very large right atrium. About 50% of individuals with Ebstein's anomaly have evidence of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, secondary to the atrialized right ventricular tissue. | |||
Other abnormalities that can be seen on the ECG include | |||
#signs of right atrial enlargement or tall and broad 'Himalayan' P waves, | |||
#first degree atrioventricular block manifesting as a prolonged PR-interval | |||
#low amplitude QRS complexes in the right precordial leads | |||
#atypical right bundle branch block | |||
#T wave inversion in V1-V4 and Q waves in V1-V4 and II, III and aVF. | |||
#Q waves in II, III, AVF. These Q waves are thought to reflect fibrotic thinning of the right ventricular free wall and/or septal fibrosis with coexisting left posterior hemiblock<cite>khairy</cite> | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Left and right bundle branch block== | |||
See: [[Conduction_delay|Conduction delay]] | See: [[Conduction_delay|Conduction delay]] | ||
| Line 161: | Line 182: | ||
==Cocaine Intoxication== | ==Cocaine Intoxication== | ||
|<!--col1-->[[Image:JJ00001.jpg|200px]] | |<!--col1-->[[Image:JJ00001.jpg|200px]] | ||
==Sarcoidosis== | |||
In patients with proven pulmonary sarcoidosis ECG changes can be used as a marker of cardiac involvement. Presence of a fractionated QRS or a Bundle Branch Block increases the likelihood of cardiac involvement.<cite>schuller</cite> | |||
{{Box| | {{Box| | ||
| Line 171: | Line 195: | ||
#Maron pmid=14681516 | #Maron pmid=14681516 | ||
#hypoth pmid=2738372 | #hypoth pmid=2738372 | ||
#khairy pmid=18056539 | |||
#schuller pmid=21615816 | |||
#bb pmid=10866327 | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:ECG Textbook]] | [[Category:ECG Textbook]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:26, 31 May 2012
| Author(s) | I.A.C. van der Bilt, MD | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Medication
Digoxin
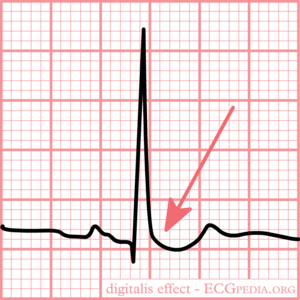
ECG changes typical for digoxin use (digoxin = Lanoxin) are:
- Oddly shaped ST-depression with 'scooped out' appearance of the ST segment (see figure)
- Flat, negative or biphasic T wave
- Short QT interval
- Increased u-wave amplitude
- Prolonged PR-interval
- Sinus bradycardia
ECG changes typical for digoxin intoxication are:
- Bradyarrhythmias:
- AV block. Including complete AV block and Wenkebach.
- Tachyarrhythmias:
- Junctional tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia
- Ventricular ectopia, bigemini, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia
Intoxication can lead to an SA-block or AV-block, sometimes in combination with tachycardia. NB these effects are increased by hypokalemia. In extreme high concentrations rhythm disturbances (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation) may develop.
Antiarrhythmics
- Anti-arrhythmics: These may lead to several ECG-changes;
- Broad and irregular P-wave
- Broad QRS complex
- Prolonged QT interval (brady-, tachycardia, AV-block, ventricular tachycardia)
- Prominent U-wave
- In case of intoxication, the above mentioned characteristics are more prominent
Additionally, several arrhthytmias can be seen.
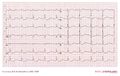
Beta blockers

Beta blocker intoxication can result in bradycardia, hypotension, QRS widening and seizures. In a series of 260 patients with beta blocker intoxication, 41 (15%) developed cardiovascular morbidity and 4 (1.4%) died. Cardioactive coingestant (e.g. calcium channel blockers) was the only factor significantly associated with the development of cardiovascular morbidity. bb
Nortriptyline Intoxication
Amitriptyline Intoxication
 |
 |
Pericarditis
Myocarditis

Myocarditis is an inflammation of the myocardium and the interstitium. The symptoms are faint chest pain, abnormal heart rate and progressive heart failure. It can be caused by several factors: viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, spirochetes, auto-immune reactions, borreliosis (Lyme's disease) and HIV/AIDS.
Acute peri/myocarditis causes nonspecific ST segment changes. These can be accompanied by supraventricular and ventricular rhythm disturbances and T-wave abnormalities.
Pulmonary Embolism
See the chapter Pulmonary Embolism
Chronic Pulmonary Disease Pattern

The ECG shows low voltage QRS complexes in leads I, II, and III and a right axis deviation. This is caused by the increased pressure on the right chamber. This leads to right ventricular hypertrophy.
Pacemaker
See the chapter Pacemaker
Tamponade

In case of tamponade, fluid collects in the pericardium. Because the pericardium is stiff, the heart is compressed, resulting in filling difficulties. This is a potentially life-threatening situation and should be treated with pericardiocentesis, drainage of the fluid. Tamponade can be the result of pericarditis or myocarditis. After a myocardial infarction a tamponade can also develop; this is called Dresslers' Syndrome. In case of cancer,increased pericardial fluid may develop. This is usually caused by pericarditis carcinomatosis, meaning that the cancer has spread to the pericardium
The ECG shows:
- Sinus tachycardia
- Low-voltage QRS complexes microvoltages
- Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias
- PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an atrial infarction)
Ventricular Aneurysm
The ECG pattern suggests an acute MI. All classical signs of MI may occur:; Q waves, ST segment elevations (>1mm, >4 weeks present)and T wave inversions are present. To exclude an acute MI, comparison with old ECG's is compulsory (MI has occurred years before).
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Often, a LBBB or broadened QRS-complex can be seen. Additionally, nonspecific ST segment changes are present with signs of left atrial enlargement.
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
A HOCM is a hereditary illness. On the ECG there are signs of left ventricular hypertrophy and left atrial enlargement.
Electrolyte Disturbances
See chapter: electrolyte disturbances
Hypothermia
-
A 12 lead ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 32 degrees Celsius. Note the sinus bradycardia, the prolonged QT interval (QTc is not prolonged) and the Osborn J wave, most prominently in leads V2-V5
-
An ECG of a patient with a body temperature of 28 degrees Celsius.
In hypothermia a number of specific changes can be seen;hypoth
- Sinus bradycardia
- Prolonged QTc-interval
- ST segment elevation (inferior and left precordial leads)
- Osborn-waves (slow deflections at the end of the QRS-complex)
ECG Changes after Neurologic Events

In 1938, Aschenbrenner Aschenbrenner noted that repolarization abnormalities may occur after increased intracranial pressure. Since then, many publications have described ECG changes after acute neurological events.
ECG changes that may occur are:
- Q waves
- ST segment elevations,
- ST segment depressions,
- T wave changes. Large negative T waves over the precordial leads are observed frequently.
- Prolonged QT-interval.
- Prominent u-waves.
These abnormalities are frequently seen after subarachnoid_hemorrhage (SAH) (if measured serially, almost every SAH patients has at least one abnormal ECG.), but also in subdural hematoma, ischemic CVA's, brain Tumors, Guillain Barré, epilepsy and migraine. The ECG changes are generally reversible and have limited prognostic value. However, the ECG changes can be accompanied with myocardial damage and echocardiographic changes. The cause of the ECG changes is not yet clear. The most common hypothesis is that of a neurotramitter "catecholamine storm" caused by sympathetic stimulation.
Cardiac Contusion
Cardiac contusion (in latin: contusio cordis or commotio cordis) is caused by a blunt trauma to the chest, often caused by a car or motorbike accident or in martial artsMaron. Rhythm disturbances and even heart failure can occur. Diagnosis is made using echocardiography and laboratory testing for cardiac enzymes. Possible ECG changes are:Sybrandy
Nonspecific changes
- Pericarditis-like ST elevation or PTa depression
- Prolonged QT interval
Myocardial damage
- New Q waves
- ST-T segment elevation or depression
Conduction delay
- Right bundle branch block
- Fascicular blok
- AV delay(1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree AV blok)
Arrhythmias
- Sinus tachycardia
- Atrial and ventricular extrasystoles
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Sinus bradycardia
- Atrial tachycardia
Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome
The Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome is a pre-excitation syndrome in which the atria are connected to the lower part of the AV node or bundle of His. On the ECG:
- Short PR interval, < 120 ms
- Normal QRS complex
- No delta wave
Ebstein
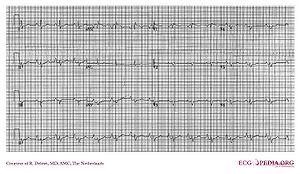
In Ebstein anomaly the tricuspid valve is inserted more apically than normal. This yields a very large right atrium. About 50% of individuals with Ebstein's anomaly have evidence of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, secondary to the atrialized right ventricular tissue.
Other abnormalities that can be seen on the ECG include
- signs of right atrial enlargement or tall and broad 'Himalayan' P waves,
- first degree atrioventricular block manifesting as a prolonged PR-interval
- low amplitude QRS complexes in the right precordial leads
- atypical right bundle branch block
- T wave inversion in V1-V4 and Q waves in V1-V4 and II, III and aVF.
- Q waves in II, III, AVF. These Q waves are thought to reflect fibrotic thinning of the right ventricular free wall and/or septal fibrosis with coexisting left posterior hemiblockkhairy
Left and right bundle branch block
See: Conduction delay
Cocaine Intoxication
Sarcoidosis
In patients with proven pulmonary sarcoidosis ECG changes can be used as a marker of cardiac involvement. Presence of a fractionated QRS or a Bundle Branch Block increases the likelihood of cardiac involvement.schuller
{{{1}}}