Technical Problems: Difference between revisions
m (→artifacts) |
m (→artifacts) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
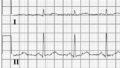
Image:BaselineDrift.png| Baseline drift. The amplifier in the ECG machine has to re-find the 'mean'. This often occurs right after lead connection and after electric cardioversion. | Image:BaselineDrift.png| Baseline drift. The amplifier in the ECG machine has to re-find the 'mean'. This often occurs right after lead connection and after electric cardioversion. | ||
Image:cardioversion_from_afib.jpg| Cardioversion from atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm, with clear baseline drift. | Image:cardioversion_from_afib.jpg| Cardioversion from atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm, with clear baseline drift. | ||
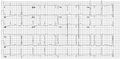
Image:electric_noise_ecg.png| Electrical interference from a nearby electrical appliance. A typical example is a 100 Hz background distortion from fluorescent lights. Not to be confused with [[ | Image:electric_noise_ecg.png| Electrical interference from a nearby electrical appliance. A typical example is a 100 Hz background distortion from fluorescent lights. Not to be confused with [[AF|atrial fibrillation]]. | ||
Image:electric_noise_ecg2.jpg| Another example of an artefact caused by an electrical appliance. The patients rhythm is regular. This strip shows 10 QRS complexes. | Image:electric_noise_ecg2.jpg| Another example of an artefact caused by an electrical appliance. The patients rhythm is regular. This strip shows 10 QRS complexes. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 20:19, 7 August 2008
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Lead reversals
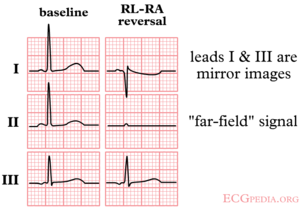
Sometimes an ECG is not made properly. Mistakes do happen and leads can be switched. Always remain careful to check this or you might come to the wrong conclusions. One of the most common mistakes is to switch the right and left arm. This will result in negative complexes in I, indicating a right axis deviation!
Common mistakes are reversal of:
- right leg and right arm:
- Hardly any signal in lead II.
- right and left arm electrodes;
- reversal of leads II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVL
- left arm and left leg:
- reversal of leads I and II
- reversal of leads aVR and aVF
- inversion of lead III
- right arm and left leg:
- inversion of leads I, II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVF
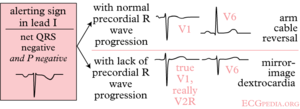
It is possible to distinguish lead reversal and dextrocardia by watching the precordial leads. Dextrocardia will not show any R wave progression in leads V1-V6, whereas lead reversal will.
artifacts
Electrical interference from a nearby electrical appliance. A typical example is a 100 Hz background distortion from fluorescent lights. Not to be confused with atrial fibrillation.
artifacts (disturbances) can have many causes. Common causes are:
- Movement
- Electrical interference