P Wave Morphology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{authors| | {{authors| | ||
|mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | |mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]], A. Bouhiouf, Msc | ||
|supervisor= | |supervisor= | ||
|coauthor= | |coauthor= | ||
|moderator= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | |moderator= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | ||
|editor= | |editor= | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 5 January 2008
| «Step 4:Heart axis | Step 6: QRS morphology» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD, A. Bouhiouf, Msc | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
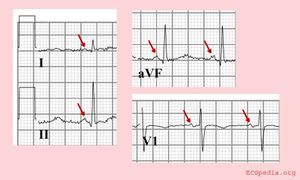
The p wave morphology can reveal right or left atrial stretch.
The P-wave morphology is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm.
The normal P wave
| Characteristics of a normal p wave:[1] |
|---|
|
Elevation or depression of the PTa segment (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from Atrial infarction or pericarditis.
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged.