Clinical Disorders: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
==Tamponade== | ==Tamponade== | ||
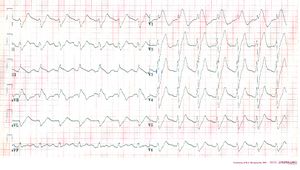
In case of a tamponade, fluid collects in the pericardium. | [[Image:PulsusAlternans.jpg|thumb]] | ||
In case of a tamponade, fluid collects in the pericardium. As the pericardium is stiff, the heart is compressed resulting in relaxation, and thus, filling difficulties. This is a potential life-threatening situation and should be treated with pericardiocenteses, which is drainage of the fluid. Tamponade can be the results of pericarditis or myocarditis. Also, after a myocardial infarction a tamponade may develop, this is called Dresslers' Syndrome. In case of cancer, pericardial fluid may develop. This is usually caused by a Pericarditis carcinomatosa, meaning that the cancer has spread to the pericardium | |||
The ECG shows: | |||
*Sinus tachycardia | *Sinus tachycardia | ||
*Low-voltaged QRS complexes [[microvoltages]] | *Low-voltaged QRS complexes [[microvoltages]] | ||
*Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias | *Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias | ||
*PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an [[Ischemia#Atriaal_.2F_boezem_infarct|atrial infarction]]) | *PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an [[Ischemia#Atriaal_.2F_boezem_infarct|atrial infarction]]) | ||
{{clr}} | |||
==Ventricular Aneurysm== | ==Ventricular Aneurysm== | ||
Revision as of 11:03, 24 September 2007
| Author(s) | I.A.C. van der Bilt, MD | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Medication
Digoxin
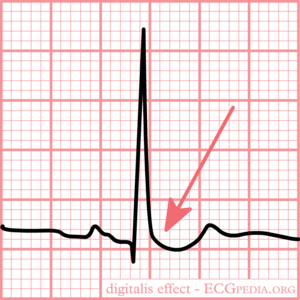
ECG changes typical for digoxin intoxication (digoxin = Lanoxin) are:
- odd shaped ST-depression.
- T-wave flat, negative or biphasic
- Short QT interval
- Increased u-wave amplitude
- Prolonged PR-interval
- Brady-arrhytmias:
- Sinusbradycardia
- AV block. Including complete AV block and Wenkebach.
- Tachyarrhythmias:
- Junctional tachycardia
- Atrialtachycardia
- Ventricular ectopia, bigemini, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, bidirectional ventricular tachycardia
Intoxication can lead to a SA-block or AV-block, sometimes in combination with a tachycardia. NB these effects are increased by hypokaliemia. In extreme high concentrations rhythmdisturbances (ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, atrial fibrillation) may develop.
Anti-arhythmics
- anti-arhythmics: These may lead to several ECG-changes;
- broad and irregulair P-wave
- broad QRS-complex
- prolonged QT-interval (brady-, tachycardia, AV-block, ventricular tachycardia)
- prominent U-wave
- In case of intoxication, the above mentioned characteristics are more prominent
Additionally, several arrhtythmias can be seen.
Nortriptyline intoxication
Amitriptyline intoxication
Pericarditis
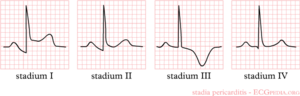
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium. This can lead to ST elevation in all leads. Therefore, it is important to distinguish pericarditis from a myocardial infarction, which has more acute complaints and ST-elevations are limited to the infarct area.
In pericarditis four stages can be used:
- stage I: ST elevation in all leads. PTa depression (depression between the end of the P-wave and the beginning of the QRS- complex)
- stage II: pseudonormalisation (transition)
- stage III: inverted T-waves
- stage IV: normalisation
Keep into account that in stage I pericarditis, ST-elevation is present in all leads except in aVR, V1 and III.
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the myocardium and the interstitium. The symptoms are faint chestpain, abnormal heartrate and progressive heartfailure. It can be caused by several factors: viral, bacterial, fungi, parasites, spirochaet, auto-immune, borreliosis (Lyme's disease) and HIV/AIDS.
Acute peri/myocarditis causes aspecific ST changes. These can be accompanied with supraventricular and ventricular rhythmdisturbances and T-wave abnormalities.
Pulmonary embolism
In case of a pulmonary embolism several clinical features may be present:[1]
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Stress on the right ventricle:
- right atrial dilatation
- Heartaxis is to the right
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
"S1Q3T3"
- Deep S in I
- Q and negative T in III
- T wave inversion anterior [2]
Pulmonary embolism cannot solely be diagnosed using an ECG, but it may be helpful.
References
- Rodger M, Makropoulos D, Turek M, Quevillon J, Raymond F, Rasuli P, and Wells PS. Diagnostic value of the electrocardiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol. 2000 Oct 1;86(7):807-9, A10. DOI:10.1016/s0002-9149(00)01090-0 |
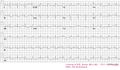
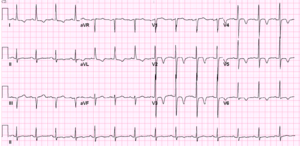
Chronic pulmonary disease pattern
The ECG shows low voltaged QRS-complexes in leads I, II, and III and a right axisdeviation. This is caused by the increased pressure on the right chamber. This leads to right ventricular hypertrophy.
Pacemaker
See the chapter Pacemaker
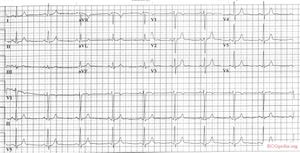
Tamponade
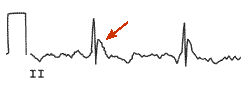
In case of a tamponade, fluid collects in the pericardium. As the pericardium is stiff, the heart is compressed resulting in relaxation, and thus, filling difficulties. This is a potential life-threatening situation and should be treated with pericardiocenteses, which is drainage of the fluid. Tamponade can be the results of pericarditis or myocarditis. Also, after a myocardial infarction a tamponade may develop, this is called Dresslers' Syndrome. In case of cancer, pericardial fluid may develop. This is usually caused by a Pericarditis carcinomatosa, meaning that the cancer has spread to the pericardium
The ECG shows:
- Sinus tachycardia
- Low-voltaged QRS complexes microvoltages
- Alternation of the QRS complexes, usually in a 2:1 ratio. Electrical alternans can also be seen in myocardial ischemia, acute pulmonary embolism, and tachyarrhythmias
- PR segment depression (this can also be observed in an atrial infarction)
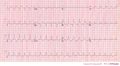
Ventricular Aneurysm
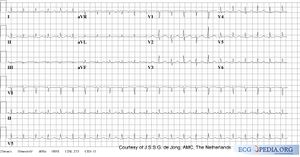
The ECG pattern suggests an acute MI. All classical signs of MI may occur:; Q-waves, ST-elevations (>1mm, >4 weeks present)and T-wave inversions are present. To exclude an acute MI, comparison with old ECG's is compulsory (MI has occurred years before).
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Often, a LBBB or broadened QRS-complex can be seen. Additionally, aspecific ST changes are present with signs of left atrial enlargement.
Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy
A HOCM is an heditary illness. On the ECG there are signs of left ventricular hypertrophy and left atrial enlargement.
Electrolyte disturbances
See chapter: electrolyte disturbances
Hypothermia
In hypothermia a number of specific changes can be seen;[3]
- sinubradycardia
- prolonged QTc-interval
- ST-elevation (inferior and left precordial leads)
- Osborne-waves (slow deflexions at the end of the QRS-complex)
ECG changes after neurologic events
In 1938, Aschenbrenner [4] noted that repolarisation abnormalities may occur after increased intracranial pressure. Since then, many publications have occurred discribing ECG changes after acute neurological events.
De ECG changes that may occur are:
- q-waves
- ST-elevations,
- ST-depressions,
- T-wave changes. Large negative T waves over the precordial leads are observed frequently.
- prolonged QT-interval.
- prominent u-waves.
These abnormalites are frequently seen after subarachnoid_hemorrhage (SAH) (if measured serially, almost every SAH patients has at least one abnormal ECG.), but also in subdural haematoma, ischemic CVA's, brain Tumors, Guillain Barré, epilepsy and migraine. The ECG changes are generally reversible and have linited prognostic value. However, the ECG changes can be accompanied with myocardial damage and echocardiographic changes. The cause of the ECG changes is not yet cl;ear. The most common hypothesis is that of a neurotramittor "catecholaminestorm" caused by sympathtic stimulation.
Cardiac contusion
Cardiac contusion (in latin: contusio cordis or commotio cordis) is caused by a blunt trauma to the chest, often caused by a car- or motorbikeaccident or in martial arts[5]. Rhythmdisturbances may occur and even heartfailure. Diagnosis is made using echocardiography and laboratorytesting for cardiac enzymes. Possible ECG changes are:[6]
Not-specific changes
- Pericarditis-like ST elevation or PTa depression
- Prolonged QT interval
Myocardial damage
- New Q waves
- ST-T segment elevation or depression
Conduction delay
- Right bundelbranchblok
- Fascicular blok
- AV delay(1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree AV blok)
Arrhythmias
- Sinustachycardia
- Atrial and ventricular extrasystoles
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Sinusbradycardia
- Atriala tachycardia
Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome
The Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome is a pre-excitation syndrome in which the atria are connected to the lower part of the AV node or bundle of His. On the ECG:
- short PR interval, < 120 ms
- normal QRS complex
- no delta wave
Left and right bundelbranch block
See: Conduction delay
References
- Rodger M, Makropoulos D, Turek M, Quevillon J, Raymond F, Rasuli P, and Wells PS. Diagnostic value of the electrocardiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol. 2000 Oct 1;86(7):807-9, A10. DOI:10.1016/s0002-9149(00)01090-0 |
- Ferrari E, Imbert A, Chevalier T, Mihoubi A, Morand P, and Baudouy M. The ECG in pulmonary embolism. Predictive value of negative T waves in precordial leads--80 case reports. Chest. 1997 Mar;111(3):537-43. DOI:10.1378/chest.111.3.537 |
- Solomon A, Barish RA, Browne B, and Tso E. The electrocardiographic features of hypothermia. J Emerg Med. 1989 Mar-Apr;7(2):169-73. DOI:10.1016/0736-4679(89)90265-5 |
-
Aschenbrenner R, Bodechtel G, Über Ekg.-Veränderungen bei Hirntumorkranken. Journal of Molecular Medicine, 17, 9, 2/1/1938, Pages 298-302, http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01778563
- Ashrafian H. Sudden death in young athletes. N Engl J Med. 2003 Dec 18;349(25):2464-5; author reply 2464-5. DOI:10.1056/NEJM200312183492518 |
- Sybrandy KC, Cramer MJ, and Burgersdijk C. Diagnosing cardiac contusion: old wisdom and new insights. Heart. 2003 May;89(5):485-9. DOI:10.1136/heart.89.5.485 |