P Wave Morphology: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{authors| | {{authors| | ||
|mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | |mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 20 May 2007
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
The p wave morphology can reveal right or left atrial stretch.
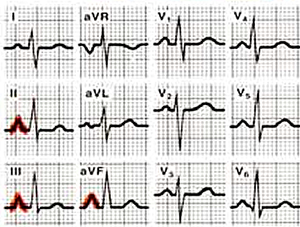
The P-wave morphology is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm.
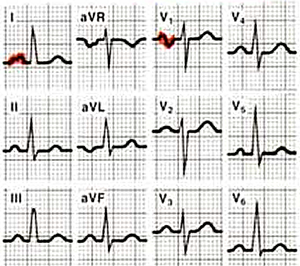
The normal P wave
Characteristics of a normal p wave:[1]
- The maximal height of the P wave is 2.5 mm in leads II and / or III
- The p wave is positive in II and AVF, and bifasic in V1
- The p wave duration is usually shorter than 0.12 seconds
Elevation or depression of the PTa segment (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from Atrial infarction or pericarditis.
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged.
Left atrial enlargement
- Criteria for left atrial voor left atrial enlargement. Either
- P wave with a broad (>0,04 sec or 1 small square) and deeply negative (>1 mm) terminal part in V1
- P wave duration >0,12 sec in laeds I and / or II
Left atrial enlargement is often seen in mitral valve insufficiency, resulting in backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium and subsequent incresed local pressure.
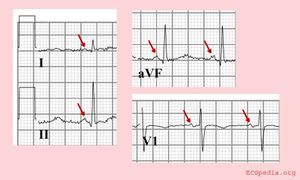
Right atrial enlargement
- Right atrial enlargement is defined as either
- P >2,5 mm in II / III and / or aVF
- P >1,5 mm in V1.
Right atrial enlargement can result from increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, e.g. after pulmonary embolisation. A positive part of the biphasic p-wave in lead V1 larger than the negative part indicates right atrial enlargement. The width of the p wave does not change.
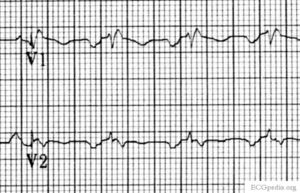
Biatrial enlargement
- Biatrial enlargement
- Biphasic p wave in V1 of more than 0.04 sec duration. The positive initial part is > 1.5mm and the negative terminal part > 1mm
In biatrial enlargement is the ECG whos signs of both left and right atrial enlargement. In V1 the p wave has large peaks first in positive and later in negative direction.
Referenties
- Spodick DH, Raju P, Bishop RL, and Rifkin RD. Operational definition of normal sinus heart rate. Am J Cardiol. 1992 May 1;69(14):1245-6. DOI:10.1016/0002-9149(92)90947-w |
<analytics uacct="UA-807577-6"></analytics>