Intraventricular Conduction: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Conduction delay== | ==Conduction delay== | ||
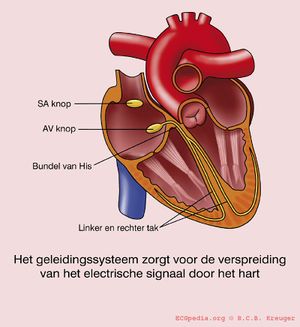
[[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb| If the conduction system is dysfunctional, the QRS widens beyond 0.12 seconds.]] | [[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb| If the conduction system is dysfunctional, the QRS widens beyond 0.12 seconds.]] | ||
If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of | If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of one of the bundle branches: | ||
*[[# | *[[#LBBB| Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB))]] | ||
*[[# | *[[#RBBB| Right Bundle Branch Block(RBBB)]] | ||
*Interventricular conduction delay | *Interventricular conduction delay | ||
A right or left axis rotation can be caused by a: | A right or left axis rotation can be caused by a: | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*[[#Criteria for LPFB| left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)]] | *[[#Criteria for LPFB| left posterior fascicular block (LPFB)]] | ||
Sometimes this conduction delay is '''frequency- | Sometimes this conduction delay is '''frequency-dependent ''': the bundle branch block occurs only at higher heart rates and disappears at slower heart rates. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
== | == LBBB vs RBBB == | ||
Check V1 for QRS > 0,12 sec. | |||
When the last QRS in V1 is below the baseline (moving away from V1), a LBBB is the most likely diagnosis. | |||
When the last activity is above the baseline, it's a RBBB | |||
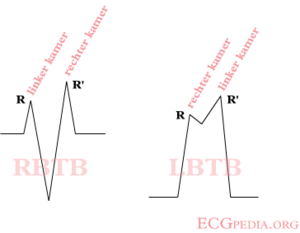
[[Image:Verschil_LBTB-RBTB.png|thumb| A bundle branch block causes a delay in the | [[Image:Verschil_LBTB-RBTB.png|thumb| A bundle branch block causes a delay in the depolarization of the right (RBBB) or left (LBBB) ventricle. In RBBB the QRS complex shows a second peak or R' in V1.]] | ||
If the QRS > 0.12 sec. but | If the QRS > 0.12 sec. but the morphological criteria of LBBB or RBBB do not apply, it is called 'interventriculair conduction delay', a general term. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=== | ===LBBB=== | ||
Left | Left Bundle Branch Block | ||
QRS >0,12 sec with a broad R in I, aVL, V5 and V6 and missing Q wave. | |||
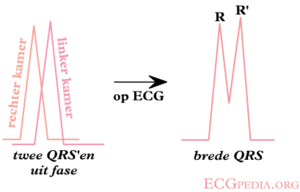
[[Image:Ontstaan_LBTB.png|thumb| | [[Image:Ontstaan_LBTB.png|thumb| In a LBBB, the left ventricle is depolarized later than the right ventricle.]] | ||
[[Image:LBBB.png|thumb| | [[Image:LBBB.png|thumb| In a LBBB, the last depolarization wave is in the left ventricle. This wave is directed away from V1. On the ECG, V1 will show a negative complex.]] | ||
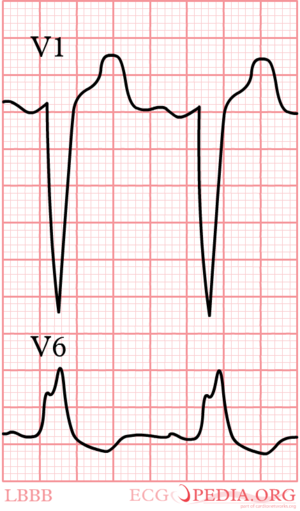
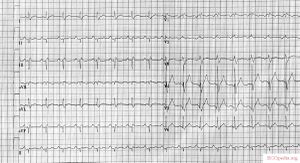
[[Image:12leadLBTB.png|thumb| | [[Image:12leadLBTB.png|thumb| Left bundle branch Block on a 12 lead ECG.]] | ||
Bij een '''linker bundeltakblok''' (LBTB), is de geleiding door de linker bundel vertraagd. Het begin van de depolarisatie is normaal, maar de laterale wand van de linker ventrikel depolariseert dus sterk vertraagd. Hierdoor is er nog electrische activiteit in de linker ventrikel op het moment dat de rest van het hart al 'klaar' is, deze wordt dus niet meer geneutraliseerd door de rechter ventrikel. De laatste activiteit gaat dus naar links, ofwel van V1 af. Met deze kennis is een LBTB makkelijk te begrijpen. Het resultaat ziet er als volgt uit: | Bij een '''linker bundeltakblok''' (LBTB), is de geleiding door de linker bundel vertraagd. Het begin van de depolarisatie is normaal, maar de laterale wand van de linker ventrikel depolariseert dus sterk vertraagd. Hierdoor is er nog electrische activiteit in de linker ventrikel op het moment dat de rest van het hart al 'klaar' is, deze wordt dus niet meer geneutraliseerd door de rechter ventrikel. De laatste activiteit gaat dus naar links, ofwel van V1 af. Met deze kennis is een LBTB makkelijk te begrijpen. Het resultaat ziet er als volgt uit: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=== | ===Right bundle branch block === | ||
QRS >0,12 sec. met RSR'-patroon in V1V2 waarbij R' >R. | QRS >0,12 sec. met RSR'-patroon in V1V2 waarbij R' >R. | ||
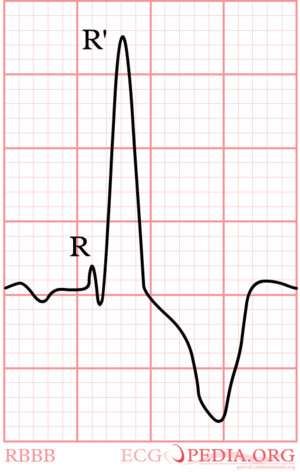
[[Image:RBBB.png|thumb| | [[Image:RBBB.png|thumb| Right bundle btanch Block (RBBB), hier in V1]] | ||
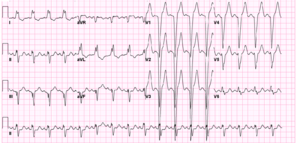
[[Image:ECG_RBTB_LAtrD.jpg|thumb| Een ECG met Rechter bundeltakblok (en linker atriumdilatatie)]] | [[Image:ECG_RBTB_LAtrD.jpg|thumb| Een ECG met Rechter bundeltakblok (en linker atriumdilatatie)]] | ||
Door in V1 te kijken, kan je deze opties onderscheiden. | Door in V1 te kijken, kan je deze opties onderscheiden. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
===Criteria | ===Criteria for LAFB=== | ||
Bij een linker anterior fascie blok is de voorste bundel van de twee linker bundels geblokkeerd. Hierdoor wordt de voorwand als laatste ontladen. Dit uit zich in een linker asdraai. De QRS-duur is <0,12 seconde. | Bij een linker anterior fascie blok is de voorste bundel van de twee linker bundels geblokkeerd. Hierdoor wordt de voorwand als laatste ontladen. Dit uit zich in een linker asdraai. De QRS-duur is <0,12 seconde. | ||
asdeviatie naar links (<-30°); | asdeviatie naar links (<-30°); | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
S >R in II, III; | S >R in II, III; | ||
QRS niet of slechts in geringe mate verbreed. | QRS niet of slechts in geringe mate verbreed. | ||
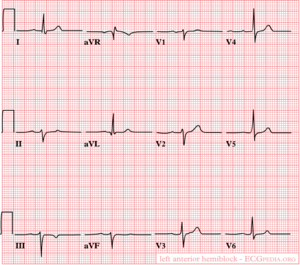
[[Image:LAHB.png|thumb| | [[Image:LAHB.png|thumb| Left anterior hemiblock]] | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
===Criteria | ===Criteria for LPFB=== | ||
Criteria voor een posterior fascie blok: | Criteria voor een posterior fascie blok: | ||
asdeviatie naar rechts >+120°; | asdeviatie naar rechts >+120°; | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 19 May 2007
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Conduction delay
If the QRS complex is wider than 0.12 seconds this is mostly caused by a delay in the conduction tissue of one of the bundle branches:
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB))
- Right Bundle Branch Block(RBBB)
- Interventricular conduction delay
A right or left axis rotation can be caused by a:
Sometimes this conduction delay is frequency-dependent : the bundle branch block occurs only at higher heart rates and disappears at slower heart rates.
LBBB vs RBBB
Check V1 for QRS > 0,12 sec. When the last QRS in V1 is below the baseline (moving away from V1), a LBBB is the most likely diagnosis. When the last activity is above the baseline, it's a RBBB
If the QRS > 0.12 sec. but the morphological criteria of LBBB or RBBB do not apply, it is called 'interventriculair conduction delay', a general term.
LBBB
Left Bundle Branch Block QRS >0,12 sec with a broad R in I, aVL, V5 and V6 and missing Q wave.
Bij een linker bundeltakblok (LBTB), is de geleiding door de linker bundel vertraagd. Het begin van de depolarisatie is normaal, maar de laterale wand van de linker ventrikel depolariseert dus sterk vertraagd. Hierdoor is er nog electrische activiteit in de linker ventrikel op het moment dat de rest van het hart al 'klaar' is, deze wordt dus niet meer geneutraliseerd door de rechter ventrikel. De laatste activiteit gaat dus naar links, ofwel van V1 af. Met deze kennis is een LBTB makkelijk te begrijpen. Het resultaat ziet er als volgt uit:
Right bundle branch block
QRS >0,12 sec. met RSR'-patroon in V1V2 waarbij R' >R.
Door in V1 te kijken, kan je deze opties onderscheiden.
Bij een rechter bundeltakblok (RBTB) is het precies andersom. Er is nog electrische activiteit in de rechter ventrikel, terwijl de rest van het hart al 'klaar' is. De laatste activiteit gaat dus naar rechts, ofwel naar V1 toe.
Criteria for LAFB
Bij een linker anterior fascie blok is de voorste bundel van de twee linker bundels geblokkeerd. Hierdoor wordt de voorwand als laatste ontladen. Dit uit zich in een linker asdraai. De QRS-duur is <0,12 seconde.
asdeviatie naar links (<-30°); geen of vrijwel geen S in I alwaar normale kleine q; S >R in II, III; QRS niet of slechts in geringe mate verbreed.
Criteria for LPFB
Criteria voor een posterior fascie blok:
asdeviatie naar rechts >+120°; diepe S in I; kleine q in III; QRS niet of slechts in geringe mate verbreed; criteria voor RVH of oud lateraal myocardinfarct mogen niet aanwezig zijn.