Ventricular Tachycardia: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
*'''Biphasic VT''': a ventricular tachycardia with a QRS complex that alternates from beat to beat. Associated with [[Miscellaneous#Digoxin|digoxin intoxication]] and [[lqts|long QT syndrome]]. | *'''Biphasic VT''': a ventricular tachycardia with a QRS complex that alternates from beat to beat. Associated with [[Miscellaneous#Digoxin|digoxin intoxication]] and [[lqts|long QT syndrome]]. | ||
Ventricular tachycardia can be difficult to diagnose when confronted with a wide complex tachycardia. A seperate chapter deals with [[Approach_to_the_Wide_Complex_Tachycardia|ECG algorithms to | Ventricular tachycardia can be difficult to diagnose when confronted with a wide complex tachycardia. A seperate chapter deals with [[Approach_to_the_Wide_Complex_Tachycardia|ECG algorithms to analyze wide complex tachycardias]]. | ||
==Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia== | ==Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia== | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 15 April 2013
| This is part of: Ventricular Arrhythmias |
Ventricular tachycardia is defined as a sequence of three or more ventricular beats. The frequency must by higher than 100 bpm, mostly it is 110-250 bpm.
Ventricular tachycardias often origin around old scar tissue in the heart, e.g. after myocardial infarction. Also electrolyte disturbances and ischemia can cause ventricular tachycardias. The cardiac output is often strongly reduced during VT resulting in hypotension and loss of conciousness. VT is a medical emergency as it can deteriorate into Ventricular fibrillation and thus mechanical cardiac arrest.
Ventricular tachycardia can be catechorized as follows:
- Non-sustained VT: three or more ventricular beats with a maximal duration of 30 seconds.
- Sustained VT: a VT of more than 30 seconds duration (or less if treated by electrocardioversion within 30 seconds).
- Monomorphic VT: all ventricular beats have the same configuration.
- Polymorphic VT: the ventricular beats have a changing configuration. The RR interval is 180-600 ms (comparable to a heart rate of 100-333 bpm).
- Biphasic VT: a ventricular tachycardia with a QRS complex that alternates from beat to beat. Associated with digoxin intoxication and long QT syndrome.
Ventricular tachycardia can be difficult to diagnose when confronted with a wide complex tachycardia. A seperate chapter deals with ECG algorithms to analyze wide complex tachycardias.
Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia
The localisation of the origin (or exit site) of a ventricular tachycardia can be helpful in understanding the cause of the VT and is very helpful when planning an ablation procedure to treat a ventricular tachycardia. Localisation of the origin of a ventricular tachycardia is discussed in a seperate chapter.
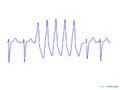
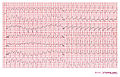
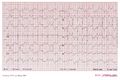
Examples
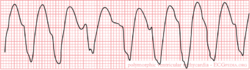
Ventricular tachycardia of 140 bpm with a left bundle branch block pattern and left heart axis.
Ventricular tachycardia of 250 bpm with a right bundle branch block pattern and right heart axis.
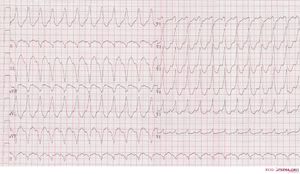
Ventricular tachycardia of 150 bpm with a right bundle branch block pattern and right heart axis. Mind the 5th and 6th complex from the right side. These are fusion complexes. Furthermore this ECG shows baseline drift, which is a technical artefact
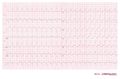
Ventricular tachycardia of 145 bpm with a right bundle branch block pattern and left heart axis.
References
- Segal OR, Chow AW, Wong T, Trevisi N, Lowe MD, Davies DW, Della Bella P, Packer DL, and Peters NS. A novel algorithm for determining endocardial VT exit site from 12-lead surface ECG characteristics in human, infarct-related ventricular tachycardia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007 Feb;18(2):161-8. DOI:10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.00721.x |