Answer Case 4: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (New page: {{Case| |previouspage= Case 3 |previousname= Case 3 |nextpage= Case 5 |nextname= Case 5}} thumb| The ECG {{clr}} Try to interprete this ECG using the 7+2 step method...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|nextpage= Case 5 | |nextpage= Case 5 | ||
|nextname= Case 5}} | |nextname= Case 5}} | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Triblock.png|thumb|700px|left| The ECG]] | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Try to interprete this ECG using the 7+2 step method | Try to interprete this ECG using the 7+2 step method | ||
==Answer== | ==Answer== | ||
* Following the 7+2 steps: | * Following the 7+2 steps: | ||
**Rhythm | **Rhythm | ||
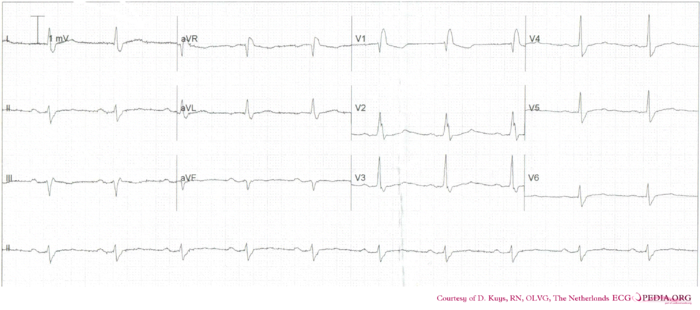
***'''The ECG | ***'''The ECG starts with a regular rhythm with normal P waves (positive in I, III and AVF, negative in AVR), followed by QRS complexes. Sinusrhythm''' | ||
**Heart rate | **Heart rate | ||
***'''around 60 bpm''' | ***'''around 60 bpm''' | ||
Latest revision as of 15:38, 11 November 2008
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
Try to interprete this ECG using the 7+2 step method
Answer
- Following the 7+2 steps:
- Rhythm
- The ECG starts with a regular rhythm with normal P waves (positive in I, III and AVF, negative in AVR), followed by QRS complexes. Sinusrhythm
- Heart rate
- around 60 bpm
- Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT)
- PQ: 240ms QRS: 120ms QT: 440ms QTc: same as QT at this heart rate
- Heartaxis
- Negative in II, III and AVF: left heart axis
- P wave morphology
- The P wave duration is somewhat prolonged.
- QRS morphology
- Wide QRS complexes with [[[RBBB|right bundle branch block]]] pattern. No LVH or pathologic Q waves.
- ST morphology
- ST depression in V1. Overall flat ST segments.
- Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step)
- Conclusion?
- Rhythm
Trifascicular block with first degree AV block, right bundle branch block and left anterior fascicular block.