P Wave Morphology
| «Step 4:Heart axis | Step 6: QRS morphology» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD, A. Bouhiouf, Msc | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
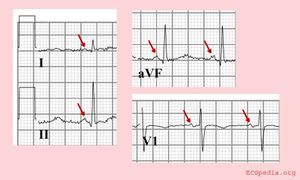
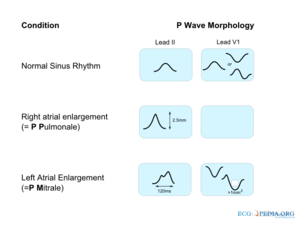
The P wave morphology can reveal right or left atrial stretch or atrial arrhythmias and is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm.
| Characteristics of a normal p wave:Spodick |
|---|
|
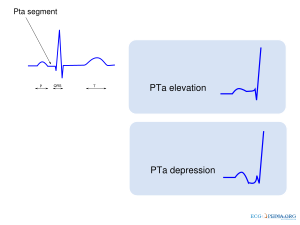
Elevation or depression of the PTa segment (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from Atrial infarction or pericarditis.
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged.
If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an ectopic atrial rhythm not originating from the sinus node.
Examples
{{{1}}}