Pathologic Q Waves
Criteria for a previous myocardial infarction

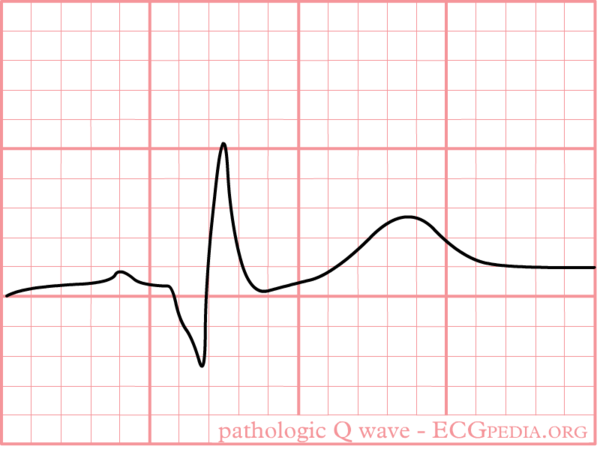
Note: Absence of pathologic Q waves does not exclude a myocardial infarction!
Pathologic Q waves are a sign of absence of electrical activity. They can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole'. Myocardial infarction results in scar tissue that is electrically dead and can therefore result in pathologic Q waves.
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. The Minnesota Code Classification System for Electrocardiographic Findings contains a very extensive definition. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.Alpert
- Definition of a pathologic Q wave
- Any Q wave in leads V1-V3
- Q wave > or = to 30ms (0.03s) in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, V4, V4, or V6 (the Q wave changes must be present in any two contiguous lead, and be > or = 1mm in depth).
Referenties
<biblio>
- Alpert pmid=10987628
</biblio>