ST Morphology
| «Step 6: QRS morphology | Step 7+1: Compare with previous ECG» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
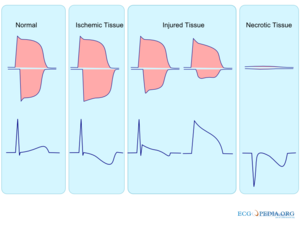
The ST segment represents ventricular repolarisation. Repolarisation follows upon contraction and depolarisation. During repolarisation the cardiomyocytes elongate and prepare for the next heartbeat. This process takes much more time than the depolarisation. Repolarisation is not passive elongation by stretch, it is an active process during which energy is consumed. On the ECG, the repolarisation phase starts at the junction, or j point, and continues until the T wave. The ST segment is normally at or near the baseline.
The T wave is usually concordant with the QRS complex. Thus if the QRS complex is positive in a certain lead (the area under the curve above the baseline is greater than the area under the curve below the baseline) than the T wave usually is positive too in that lead. Accordingly the T wave is normally upright or positive in leads I, II, AVL, AVF and V3-V6. The T wave is negative in V1 and AVR. The T wave flips around V2, but there is some genetical influence in this as in Blacks the T wave usually flips around V3.
The T wave angle is the result of small differences in the duration of the repolarisation between the endocardial and epicardial layers of the left ventricle. The endocardial myocytes need a little more time to repolarise (about 22 msec). This difference causes an electrical current from the endocardium to the epicardium, which reads as a positive signal on the ECG.[1]
ST elevation
The most important cause of ST elevation is acute Ischemia. Other causes are [3][4]:
- Early repolarization
- Acute pericarditis: ST elevation in all leads except aVR
- Pulmonary embolism: ST elevation in V1 and aVR
- Hypothermia: ST elevation in V3-V6, II, III and aVF
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: V3-V5 (sometimes V6)
- High potassium (hyperkalemia): V1-V2 (V3)
- During acute neurologic events: all leads, primarily V1-V6
- Acute sympathic stress: all leads, especially V1-V6
- Brugada syndrome.
- Cardiac aneurysm.
- Cardiac contusion
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Idioventricular rhythm including Paced rhythm
In a study by Otto et al. among 123 patients with chest paint and ST elevation of > 1 mm 63 patients did not have a myocardial infarction. Diagnoses in patients who did not have a myocardial infarction were LVH (33%) and LBBB (21%). [5] In daily practice this means that in these patients the diagnosis of myocardial infarction has to depend on other diagnostic means, such as laboratory tests, echocardiography and coronary angiography.
An important clue for the diagnosis of ischemia is the presence of reciprocal ST depression.
Early repolarization is a term used for ST elevation without underlying disease. It probably has nothing to do with actual early repolarization. It is commonly seen in young men. It is important to discern early repolariztion from ST elevation from other causes such as ischemia. Characteristics of early repolarization are:[6]
- an upward concave elevation of the RS-T segment with distinct or "embryonic" J waves
- slurred downstroke of R waves or distinct J points or both
- RS-T segment elevation commonly encountered in the precordial leads and more distinct in these leads
- rapid QRS transition in the precordial leads with counterclockwise rotation
- persistence of these characteristics for many years
- absence of reciprocal ST depression
- large symmetrical T waves
ST depression
The most important cause of ST depression is Ischemia. Other causes of ST depression are:
- Reciprocal ST depression. If one leads whos ST elevation than usually the lead 'on the other site' shows ST depression. (this is mostly seen in ischemia as well.
- Left ventricular hypertophy with "strain" or depolarization abnormality
- Digoxin effect
- Low potassium / low magnesium
- Heart rate induced changes (post tachycardial)
- During acute neurologic events.
T wave changes
The T wave is quite 'labile' and long lists of possible causes of T wave changes exist. A changing T wave can be a sign that 'something' is abnormal, but it doesn't say much about the severity. T waves can be peaked, normal, flat, or negative. Flat and negative T waves are defined as:
- flat T wave
- < 0.5 mm negative or positive T wave in leads I, II, V3, V4, V5 or V6
- negative T wave
- > 0.5 mm negative T wave in leads I, II, V3, V4, V5 or V6
A concise list of possible causes of T wave changes:
- Ischemia and myocardial infarction
- Pericarditis
- Myocarditis
- Cardiac contusion
- Acute neurologic events, such as a subarachnoid bleed.
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Digoxin effect
- Right and left ventricular hypertrophy with strain
References
- ISBN:0808923056
- Gibbons RJ, Balady GJ, Bricker JT, Chaitman BR, Fletcher GF, Froelicher VF, Mark DB, McCallister BD, Mooss AN, O'Reilly MG, Winters WL Jr, Gibbons RJ, Antman EM, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gregoratos G, Hiratzka LF, Jacobs AK, Russell RO, Smith SC Jr, and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Update the 1997 Exercise Testing Guidelines). ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for exercise testing: summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Update the 1997 Exercise Testing Guidelines). Circulation. 2002 Oct 1;106(14):1883-92. DOI:10.1161/01.cir.0000034670.06526.15 |
- Wang K, Asinger RW, and Marriott HJ. ST-segment elevation in conditions other than acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003 Nov 27;349(22):2128-35. DOI:10.1056/NEJMra022580 |
- Van de Werf F, Ardissino D, Betriu A, Cokkinos DV, Falk E, Fox KA, Julian D, Lengyel M, Neumann FJ, Ruzyllo W, Thygesen C, Underwood SR, Vahanian A, Verheugt FW, Wijns W, and Task Force on the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction of the European Society of Cardiology. Management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation. The Task Force on the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2003 Jan;24(1):28-66. DOI:10.1016/s0195-668x(02)00618-8 |
- Otto LA and Aufderheide TP. Evaluation of ST segment elevation criteria for the prehospital electrocardiographic diagnosis fo acute myocardial infarction. Ann Emerg Med. 1994 Jan;23(1):17-24. DOI:10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70002-8 |
- Kambara H and Phillips J. Long-term evaluation of early repolarization syndrome (normal variant RS-T segment elevation). Am J Cardiol. 1976 Aug;38(2):157-6. DOI:10.1016/0002-9149(76)90142-9 |