Conduction
| «Step 2: Rate | Step 4: Learn how to determine the heart axis» |
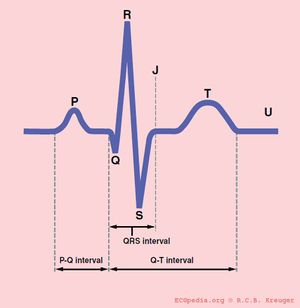
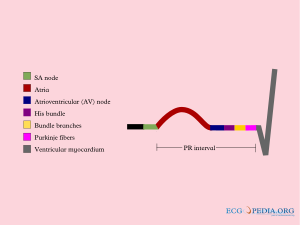
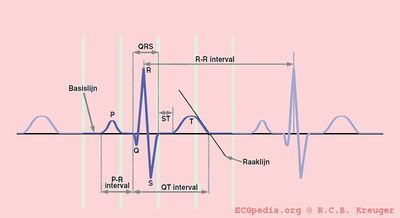
The PQ interval
The PQ interval starts at the beginning of the atrial contraction and ends at the beginning of the ventricular contraction.
The PQ interval (sometimes referred to as the PR interval as a Q wave is not always present) indicates how fast the action potential is transmitted through the AV node (atrioventricular) from the atria to the ventricles. Measurement should start at the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS segment.
The normal PQ interval is between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds.
A prolonged PQ interval is a sign of a degradation of the conduction system, increased vagal tone (Bezold-Jarisch reflex), or it can be pharmacologically induced.
This is called 1st, 2nd or 3rd degree AV block.
A short PQ interval can be seen in the WPW syndrome in which a faster connection exists between the atria and the ventricles.
The QRS duration
The QRS duration indicates how fast the ventricles depolarize. The normal QRS is < 0.10 seconds
The ventricles depolarize normally within 0.10 seconds. When this is longer than 110 miliseconds[1], this is a conduction delay. Possible causes of a QRS duration > 110 miliseconds include:
- Left bundle branch block
- Right bundle branch block
- Electrolyte Disorders
- Idioventricular rhythm and paced rhythm
For the diagnosis of LBBB or RBBB QRS duration must be >120 ms.
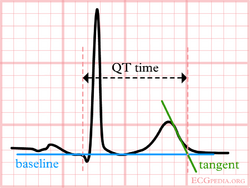
The QT interval
The normal QTc interval The QT interval indicates how fast the ventricles are repolarized and how fast they are ready for a new heart cycle.
The normal value for QTc(orrected) is: below 450ms for men and below 460ms for women. [2]
If QTc is < 340ms short QT syndrome can be considered.
The QT interval comprises the QRS-complex, the ST-segment, and the T-wave. One difficultly of QT interpretation is that the QT interval gets shorter if the heart rate increases. This can be solved by correcting the QT time for heart rate using the Bazett formula: ![]()
Thus at a heart rate of 60 bpm, the RR interval is 1 second and the QTc equals QT/1. The QTc calculator can be used to easily calculate QTc from the QT and the heart rate or RR interval.
On modern ECG machines, the QTc is given. However, the machines are not always capable in the correct determination of the end of the T wave. Therefore, it is important to check the QT time manually.
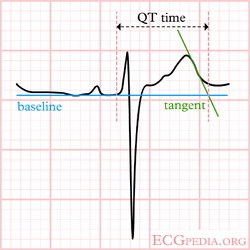
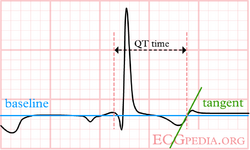
Although QT prolongation is potentially lethal, measurement of the QT interval by physicians is poor as different definitions of the end of the T wave exist.[3] Most QT experts define the end of the T wave as the intersection of the steepest tangent line from the end of the T-wave with the base line of the ECG.[4] This leads to the following stepwise approach:
| Stepwise approach to correct measurement of the QT interval |
|---|
|
In a (serious) prolonged QT time, it takes longer for the myocardial cells to be ready for a new cardiac cycle. There is a possibility that some cells are not yet repolarized, but that a new cardiac cycle is already initiated. These cells are at risk for uncontrolled depolarization and induce Torsade de Pointes and subsequent Ventricular Fibrillation.
| Causes of QT prolongation |
|---|
|
The QT interval is prolonged in congenital long QT syndrome, but QT prolongation can also occur as a consequence of (a.o.):
QT prolongation is often treated with beta blockers. |
If the QT segment is abnormal, it can be difficult to define the end of the T wave. Below are a number of examples that suggest how QT should be measured in these patients.
References
- Surawicz B, Childers R, Deal BJ, Gettes LS, Bailey JJ, Gorgels A, Hancock EW, Josephson M, Kligfield P, Kors JA, Macfarlane P, Mason JW, Mirvis DM, Okin P, Pahlm O, Rautaharju PM, van Herpen G, Wagner GS, Wellens H, American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology, American College of Cardiology Foundation, and Heart Rhythm Society. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part III: intraventricular conduction disturbances: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society: endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation. 2009 Mar 17;119(10):e235-40. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.191095 |
- Rautaharju PM, Surawicz B, Gettes LS, Bailey JJ, Childers R, Deal BJ, Gorgels A, Hancock EW, Josephson M, Kligfield P, Kors JA, Macfarlane P, Mason JW, Mirvis DM, Okin P, Pahlm O, van Herpen G, Wagner GS, Wellens H, American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology, American College of Cardiology Foundation, and Heart Rhythm Society. AHA/ACCF/HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part IV: the ST segment, T and U waves, and the QT interval: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society: endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation. 2009 Mar 17;119(10):e241-50. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.191096 |
- LEPESCHKIN E and SURAWICZ B. The measurement of the Q-T interval of the electrocardiogram. Circulation. 1952 Sep;6(3):378-88. DOI:10.1161/01.cir.6.3.378 |
-
Bazett HC. An analysis of the time-relations of electrocardiograms. Heart 1920;7:353-370.
- Gaita F, Giustetto C, Bianchi F, Wolpert C, Schimpf R, Riccardi R, Grossi S, Richiardi E, and Borggrefe M. Short QT Syndrome: a familial cause of sudden death. Circulation. 2003 Aug 26;108(8):965-70. DOI:10.1161/01.CIR.0000085071.28695.C4 |
- Moss AJ. Measurement of the QT interval and the risk associated with QTc interval prolongation: a review. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Aug 26;72(6):23B-25B. DOI:10.1016/0002-9149(93)90036-c |