P Wave Morphology
Some statements may be disputed, incorrect or biased. |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
The p wave morphology can reveal right or left atrial stretch.
The P-wave morphology is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm.
The normal P wave

Characteristics of a normal p wave:Spodick
- The maximal height of the P wave is 2.5 mm in leads II and / or III
- The p wave is positive in II and AVF, and bifasic in V1
- The p wave duration is usually shorter than 0.12 seconds
Elevation or depression of the PTa segment (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from Atrial infarction or pericarditis.
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged.
Left atrial enlargement
Criteria for left atrial voor left atrial enlargement:
P wave with a broad (>0,04 sec or 1 small square) and deeply negative (>1 mm) terminal part in V1, and / or >0,12 sec in laeds I and / or II

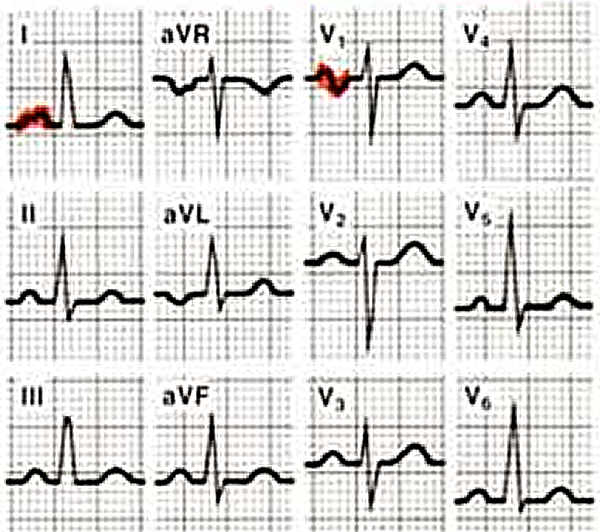

Left atrial enlargement is often seen in mitral valve insufficiency.
Right atrial enlargement
- Right atrial enlargement is defined as either
- P >2,5 mm in II / III and / or aVF
- P >1,5 mm in V1.

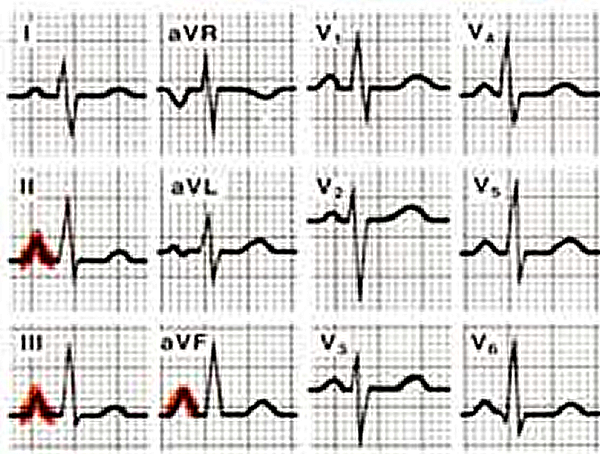
Right atrial enlargement can result from increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, e.g. after pulmonary embolisation. A positive part of the biphasic p-wave in lead V1 larger than the negative part indicates right atrial enlargement. The width of the p wave does not change.
Biatriale belasting
Bifasische P in V1 > 0.04 sec, positief initieël deel >1.5mm en een negatief terminaal deel > 1mm
Biatriale belasting vertoont op het ECG tekenen van zowel rechter- als linkeratriumhypertrofie. V1 laat een groot eerste deel van de bifasische P-top en een diep breed tweede deel van de bifaische P-top zien.
Referenties
<biblio>
- Spodick pmid=1575201
</biblio> <analytics uacct="UA-807577-6"></analytics>