Technical Problems: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
==Artifacts== | ==Artifacts== | ||
Artifacts (disturbances) can have many causes. Common causes are: | |||
* Movement | |||
* Electrical interference | |||
<gallery perRow="4"> | <gallery perRow="4"> | ||
Image:Noise_move.png|Movement artifacts | Image:Noise_move.png|Movement artifacts | ||
| Line 47: | Line 50: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 15 October 2009
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Lead reversals
Lead switches are a common mistake when ECGs are made and can lead to wrong diagnoses. Common mistakes are:
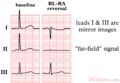
- Left - right arm reversals. This leads to a negative complex in lead I with also a negative P wave in lead I. It is one of the most common causes of right axis deviation on the ECG!
- Arm - foot switches lead to a very small or 'far field' signal in leads II or III.
- Chest lead reversal lead to inappropiate R wave progression (increase - decrease - increase) and are often easily recognized.
Therefore any right axis or small signal in an extremity lead should be reason enough to check lead positioning. A previous ECG can be very helpful.
-
Right and left arm lead reversal can be distinguished from the (much rarer) dextrocardia by looking at the precordial R wave progression.
-
Right arm and left leg lead reversal. Lead II now measures the signal between the left and right leg, which is remote from the heart.
-
A patient with dextrocardia (and previous inferior myocardial infarction)
More specific patterns with every lead reversal:
- right leg and right arm:
- Hardly any signal in lead II.
- right and left arm electrodes;
- reversal of leads II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVL
- left arm and left leg:
- reversal of leads I and II
- reversal of leads aVR and aVF
- inversion of lead III
- right arm and left leg:
- inversion of leads I, II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVF
It is possible to distinguish lead reversal and dextrocardia by watching the precordial leads. Dextrocardia will not show any R wave progression in leads V1-V6, whereas lead reversal will.
Artifacts
Artifacts (disturbances) can have many causes. Common causes are:
- Movement
- Electrical interference
-
Movement artifacts
-
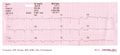
Increasing movement artifacts in a Parkinson patient. The patient was in sinus rhythm! (which doesn't show on this short recording)
-
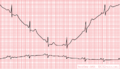
Baseline drift. The amplifier in the ECG machine has to re-find the 'mean'. This often occurs right after lead connection and after electric cardioversion.
-
Cardioversion from atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm, with clear baseline drift.
-
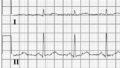
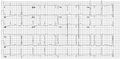
Electrical interference from a nearby electrical appliance. A typical example is a 100 Hz background distortion from fluorescent lights. Not to be confused with atrial fibrillation.
-
Another example of an artefact caused by an electrical appliance. The patients rhythm is regular. This strip shows 10 QRS complexes.
-
An artifact that was originally diagnosed as a VT