Pathologic Q Waves: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Pathologic Q waves are a sign of '''previous [[Myocardial Infarction|myocardial infarction]]'''. The are the result of absence of electrical activity. A myocardial infarction can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole' as scar tissue is electrically dead and therefore results in pathologic Q waves. Pathologic Q waves are not an early sign of myocardial infarction, but '''generally take several hours to days to develop'''. Once pathologic Q waves have developed they rarely go away. However, if the myocardial infarction is reperfused early (e.g. as a result of percutaneous coronary intervention) stunned myocardial tissue can recover and pathologic Q waves disappear. In all other situations they '''usually persist indefinitely'''. | Pathologic Q waves are a sign of '''previous [[Myocardial Infarction|myocardial infarction]]'''. The are the result of absence of electrical activity. A myocardial infarction can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole' as scar tissue is electrically dead and therefore results in pathologic Q waves. Pathologic Q waves are not an early sign of myocardial infarction, but '''generally take several hours to days to develop'''. Once pathologic Q waves have developed they rarely go away. However, if the myocardial infarction is reperfused early (e.g. as a result of percutaneous coronary intervention) stunned myocardial tissue can recover and pathologic Q waves disappear. In all other situations they '''usually persist indefinitely'''. | ||
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.<cite> | The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.<cite>Thygesen</cite> | ||
;Definition of a pathologic Q wave | ;Definition of a pathologic Q wave | ||
:Any Q-wave in leads V2–V3 >= 0.02 s or QS complex in leads V2 and V3 | |||
:Q-wave >= 0.03 s and > 0.1 mV deep or QS complex in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, or | |||
V4–V6 in any two leads of a contiguous lead grouping (I, aVL,V6; V4–V6; II, III, | |||
and aVF)* | |||
:R-wave >= 0.04 s in V1–V2 and R/S > 1 with a concordant positive T-wave in the | |||
absence of a conduction defect | |||
'''Notes''' | '''Notes''' | ||
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#Alpert pmid=10987628 | #Alpert pmid=10987628 | ||
#Thygesen pmid=17951284 | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 08:40, 8 October 2009
| This is part of: Myocardial Infarction |
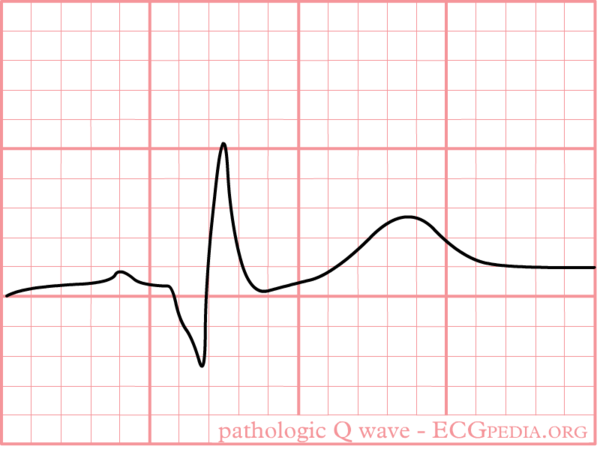
Pathologic Q waves are a sign of previous myocardial infarction. The are the result of absence of electrical activity. A myocardial infarction can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole' as scar tissue is electrically dead and therefore results in pathologic Q waves. Pathologic Q waves are not an early sign of myocardial infarction, but generally take several hours to days to develop. Once pathologic Q waves have developed they rarely go away. However, if the myocardial infarction is reperfused early (e.g. as a result of percutaneous coronary intervention) stunned myocardial tissue can recover and pathologic Q waves disappear. In all other situations they usually persist indefinitely.
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.Thygesen
- Definition of a pathologic Q wave
- Any Q-wave in leads V2–V3 >= 0.02 s or QS complex in leads V2 and V3
- Q-wave >= 0.03 s and > 0.1 mV deep or QS complex in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, or
V4–V6 in any two leads of a contiguous lead grouping (I, aVL,V6; V4–V6; II, III, and aVF)*
- R-wave >= 0.04 s in V1–V2 and R/S > 1 with a concordant positive T-wave in the
absence of a conduction defect
Notes
- Absence of pathologic Q waves does not exclude a myocardial infarction!
- Lead III often shows Q waves, which are not pathologic as long as Q waves are absent in leads II and aVF (the contiguous leads)
For those interested: the Minnesota Code Classification System for Electrocardiographic Findings contains a very extensive definition of pathologic Q waves.
References
<biblio>
- Alpert pmid=10987628
- Thygesen pmid=17951284
</biblio>