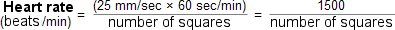Rate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|nextname=Step 3:Conduction intervals (PQ, QRS, QT, QTc) | |nextname=Step 3:Conduction intervals (PQ, QRS, QT, QTc) | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Image:ECGpapier.png|thumb| The width of a square on the ECG represents time]] | [[Image:ECGpapier.png|thumb| The width of a square on the ECG represents time]] | ||
[[Image:Ecgfreq.png|thumb| The count method to determine the heart frequency. The second QRS complex is between ''75'' and ''60'' beat per minute. This heartbeat is between that, around 65 beats per minute.]] | [[Image:Ecgfreq.png|thumb| The count method to determine the heart frequency. The second QRS complex is between ''75'' and ''60'' beat per minute. This heartbeat is between that, around 65 beats per minute.]] | ||
'''What is the heart rate?''' | |||
To answer this question, determine the time between two QRS complexes. Previously, the ECG was registered on a paperstrip transported through an ECG writer at the speed of 25 mm/second. Nowadays, digital ECG registration is common however, the method of determining the frequency remains the same. The ECG paper has a grid with thick lines 5 mm apart (= 0,20 second) and thin lines 1 mm (0,04 second). | To answer this question, determine the time between two QRS complexes. Previously, the ECG was registered on a paperstrip transported through an ECG writer at the speed of 25 mm/second. Nowadays, digital ECG registration is common however, the method of determining the frequency remains the same. The ECG paper has a grid with thick lines 5 mm apart (= 0,20 second) and thin lines 1 mm (0,04 second). | ||
Revision as of 03:50, 8 February 2009
| «Step 1: Rhythm | Step 3:Conduction intervals (PQ, QRS, QT, QTc)» |
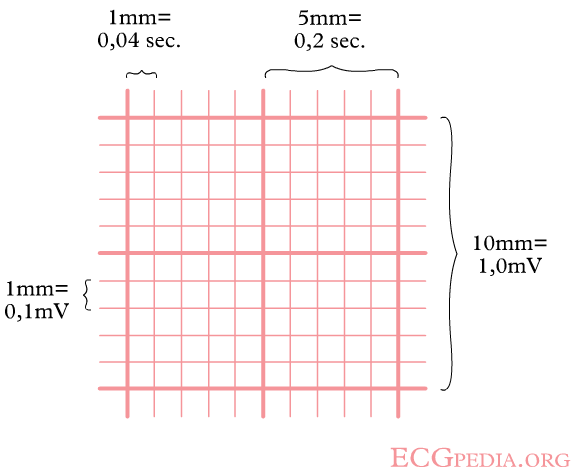
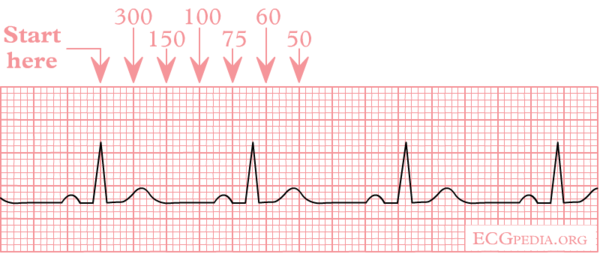
What is the heart rate? To answer this question, determine the time between two QRS complexes. Previously, the ECG was registered on a paperstrip transported through an ECG writer at the speed of 25 mm/second. Nowadays, digital ECG registration is common however, the method of determining the frequency remains the same. The ECG paper has a grid with thick lines 5 mm apart (= 0,20 second) and thin lines 1 mm (0,04 second).
| 300 | 250 | 214 | 187 | 167 | 150 | 136 | 125 | 115 | 107 | 100 | 94 | 88 | 83 | 79 | 75 | 71 | 68 | 65 | 62 | 60 |
What changes the frequency of the heart?
A number of factors change the heart frequency including:
- the (para) sympathic nerve system.
- The sympathic system e.g. epinephrin (=adrenalin) increases the atrioventricular conduction and contractility. (the fight, fright, flight reaction)
- The parasympathic system (nervus vagus) e.g. acetycholin decreases the frequency and atrioventricular conduction. The parasympathic system effects mainly the atria.
- Cardiac filling increases the frequency.
- Also arrhythmias influence heart rate.