Answer MI 18: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m Example 7 moved to Answer MI 18 |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:KJcasus7.jpg|thumb| | {{Case| | ||
|previouspage= MI 17 | |||
|previousname= MI 17 | |||
|nextpage=MI 19 | |||
|nextname=MI 19 | |||
}} | |||
'''Where is this myocardial infarction located?''' | |||
[[Image:KJcasus7.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 18. Click on image for enlargement.]] | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Answer== | |||
* Following the 7+2 steps: | * Following the 7+2 steps: | ||
**Rhythm | **Rhythm | ||
Latest revision as of 11:20, 11 November 2008
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
Where is this myocardial infarction located?
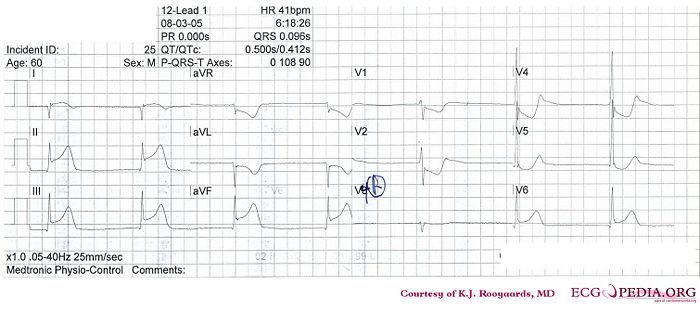
Answer
- Following the 7+2 steps:
- Rhythm
- Regular rhythm with narrow QRS complexes without P waves. Probably a nodal escape rhythm with either atrial standstill or atrial fibrillation with AV block
- Heart rate
- 41 bpm
- Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT)
- PQ: not applicable QRS: 100ms QT: 450ms QTc: 370ms
- Heartaxis
- Negative in I, positive in II and AVF, thus a right axis deviation.
- P wave morphology
- No P waves present.
- QRS morphology
- Narrow QRS, no pathologic Q waves, normal precordial R wave progression. A notch is seen in the terminal part of the QRS complex in V5/V6.
- ST morphology
- ST elevation in I, II, III, AVF, V6. ST depression in AVR, AVL, V1-V5. No ST deviation in V4R
- Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step)
- Conclusion?
- Rhythm
Inferior-posterior-lateral myocardial infarction with a nodal escape rhythm - probably due to RCX occlusion