LBBB: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[MI Diagnosis in LBBB|Diagnosis of myocardial infarction in LBBB]] is difficult as the ST segment is allways abnormal. | [[MI Diagnosis in LBBB|Diagnosis of myocardial infarction in LBBB]] is difficult as the ST segment is allways abnormal. | ||
Also read [[RBBB|richt bundle branch block]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
Revision as of 05:22, 14 August 2007
- Criteria for left bundle branch block (LBBB) Garcia
- QRS >0,12 sec
- Broad monomorphic R waves in I and V6 with no Q waves
- Broad monomorphic S waves in V1, may have a small r wave
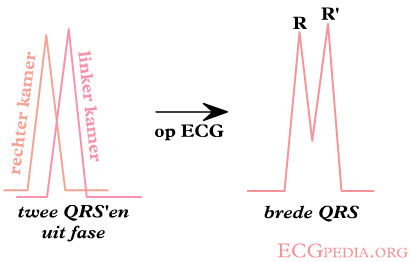
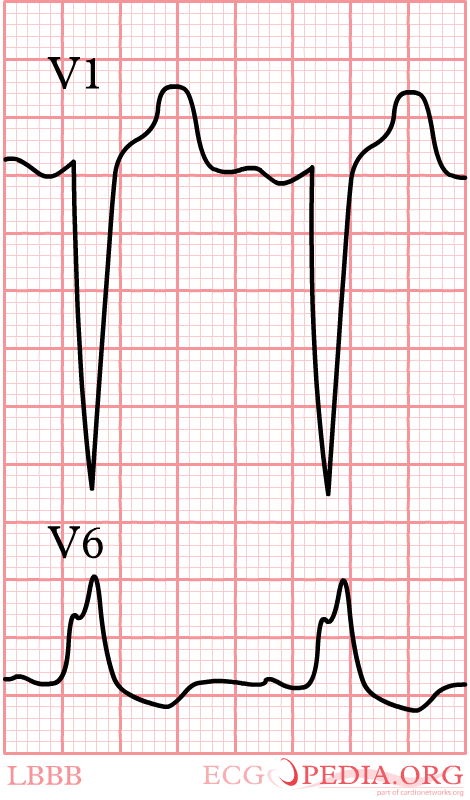
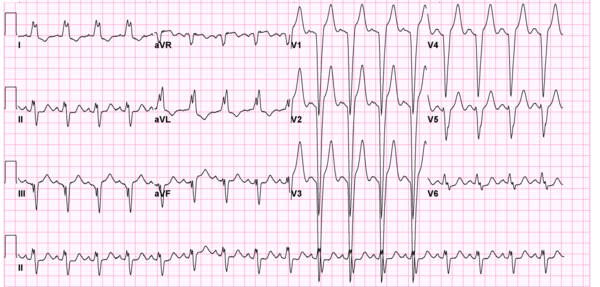
In left bundle branch block (LBBB) the conduction in the left bundle is slow. This results in delayed depolarisation of the left ventricle, especially the left lateral wall. The electrical activity in the left lateral wall is unopposed by the usual right ventricular electrical activity. The last activity on the ECG thus goes to the left or away from V1. Once you remember this, LBBB is easy to understand.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction in LBBB is difficult as the ST segment is allways abnormal.
Also read richt bundle branch block.
References
<biblio>
- Garcia isbn=0763722464
- wellens isbn=9781416002598
</biblio>