Chamber Hypertrophy and Enlargment: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Left ventricular hypertrophy== | ==Left ventricular hypertrophy== | ||
[[Image:E_lvh.jpg|thumb]] | [[Image:E_lvh.jpg|thumb]] | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:linker_ventrikel_hypertrofie.GIF|thumb]] | ||
[[Image:LVH.jpg|thumb|ECG of patient with left ventricular hypertrophy according to the Sokolow-Lyon criteria]] | [[Image:LVH.jpg|thumb|ECG of patient with left ventricular hypertrophy according to the Sokolow-Lyon criteria]] | ||
[[Image:Extreme_lvh2.jpg|thumb|Another example of extreme left ventricular hypertrophy in a patient with severe aortic valve stenosis.]] | [[Image:Extreme_lvh2.jpg|thumb|Another example of extreme left ventricular hypertrophy in a patient with severe aortic valve stenosis.]] | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 6 August 2007
In hypertrophy the heart muscle is thicker. This can have different causes. Left ventricular hypertrophy results from an increase in left ventricular workload, e.g. during hypertension or aortic valve stenosis. Right ventricular hypertrophy results from an increase in right ventricular workoad, e.g. emphysema or pulmonary embolisation. These causes are fundamentally different from hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HCM), which is a congenital misallignment of cardiomyocytes resulting in hypertrophy.
Left and right ventricular hypertrophy can be distinguished on the ECG:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
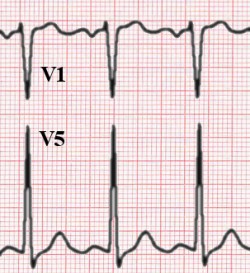



As the left ventricular becomes thicker, the QRS complexes become larger. This is especially true for leads V1-V6. The S wave in V1 is deep, the R wave in V4 is high. Often some ST depression can be seen in leads V5-V6, which is in this setting is called a 'strain pattern'.
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrhophy on the ECG one of the following criteria should be met:
- R in V5 or V6 + S in V1 >35 mm. (this is called the Sokolow-Lyon criterium)
- R >26 mm in V5 or V6;
- R >20 mm in I, II or III;
- R >12 mm in aVL (in the absence of left anterior fascicular block);
The Cornell-criterium has different values in men and women:
- R in aVL and S in V3 >28 mm in men
- R in aVL and S in V3 >20 mm in women
Right ventricular hypertrophy

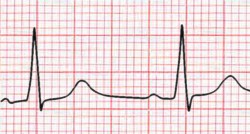
Right ventricular hypertrophy occurs mainly in lung disease or in congenital heart disease. The ECG shows a negative QRS complex in I (and thus a right heart axis) and a positive QRS complex in V1.
- R > S in V1 (R must be > 0.5 mV)
- Right heart axis
Left atrial enlargement
- Criteria for left atrial voor left atrial enlargement. Either
- P wave with a broad (>0,04 sec or 1 small square) and deeply negative (>1 mm) terminal part in V1
- P wave duration >0,12 sec in laeds I and / or II

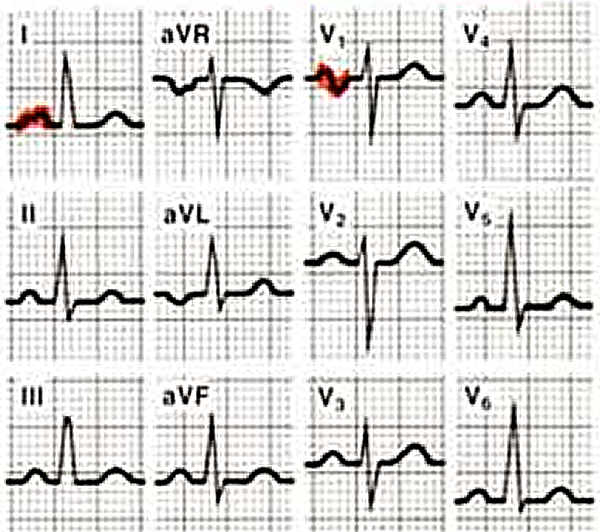

Left atrial enlargement is often seen in mitral valve insufficiency, resulting in backflow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium and subsequent incresed local pressure.
Right atrial enlargement
- Right atrial enlargement is defined as either
- P >2,5 mm in II / III and / or aVF
- P >1,5 mm in V1.

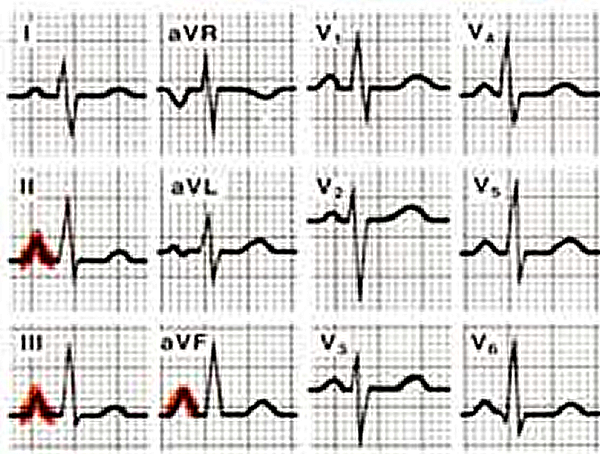
Right atrial enlargement can result from increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, e.g. after pulmonary embolisation. A positive part of the biphasic p-wave in lead V1 larger than the negative part indicates right atrial enlargement. The width of the p wave does not change.
Biatrial enlargement
- Biatrial enlargement
- Biphasic p wave in V1 of more than 0.04 sec duration. The positive initial part is > 1.5mm and the negative terminal part > 1mm
In biatrial enlargement is the ECG whos signs of both left and right atrial enlargement. In V1 the p wave has large peaks first in positive and later in negative direction.