Inferior MI: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chapter|Myocardial Infarction}} | {{Chapter|Myocardial Infarction}} | ||
'''ST elevation in II, III and aVF''' | '''ST elevation in II, III and aVF''' | ||
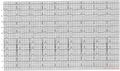
This part of the heart muscle lies on the diaphragm and is supplied of blood bij the right coronary artery (RCA) in 8% of patients. In the remaing 20% the inferior wall is supplied by the ramus circumflexus(RCX). | This part of the heart muscle lies on the diaphragm and is supplied of blood bij the right coronary artery (RCA) in 8% of patients. In the remaing 20% the inferior wall is supplied by the ramus circumflexus(RCX). | ||
[[Image:AMI_inferior.jpg|thumb| An example of an inferior waal infarction.]] | [[Image:AMI_inferior.jpg|thumb| An example of an inferior waal infarction.]] | ||
Revision as of 20:57, 22 July 2007
| This is part of: Myocardial Infarction |
ST elevation in II, III and aVF
This part of the heart muscle lies on the diaphragm and is supplied of blood bij the right coronary artery (RCA) in 8% of patients. In the remaing 20% the inferior wall is supplied by the ramus circumflexus(RCX).

An occlusion of the RCA can be distinguished of a RCX occulsuion on the ECG: in a RCA occlusion, there is ST depression in I and AvL and the ST-elevation is higher in III than in II. If the elevation is higher in II, suspect a RCX occlusion.
Examples
-
Inferior-posterior MI due to RCA occlusion
-
Inferior MI due to RCA occlusion
-
Inferior MI due to RCX occlusion
-
Posterior-lateral MI due to RCX occlusion