Anterior MI: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
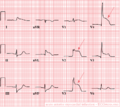
Image:AMI_anterior.png|A typical example of an acute anterior wall infarction. ST elevation in leads I, AVL and V2-V5. Reciprocal depressions in the inferior leads (II,III,AVF) | Image:AMI_anterior.png|A typical example of an acute anterior wall infarction. ST elevation in leads I, AVL and V2-V5. Reciprocal depressions in the inferior leads (II,III,AVF) | ||
Image:Ami0003.jpg|Acute MI with proximal LAD occlusion | |||
Image:ECG_VWI_2wk.jpg|A 2 weeks old anterior infarction with Q waves in V2-V4 and persisting ST elevation, a sign of formation of a [[Cardiac_Aneurysm|cardiac aneurysm]]. | Image:ECG_VWI_2wk.jpg|A 2 weeks old anterior infarction with Q waves in V2-V4 and persisting ST elevation, a sign of formation of a [[Cardiac_Aneurysm|cardiac aneurysm]]. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 20:46, 22 July 2007
| This is part of: Myocardial Infarction |
ECG-characteristics:Wung
ST-elevation in leads V1-V6, I and aVL. Maximum elevation in V3, maximal depression in III later: pathological Q-wave in the precordial leads V2 to V4-V5.

Encomprises the anterior part of the heart and a part of the ventricular septum. Is supplied by blood by the LAD.
Examples
-
A typical example of an acute anterior wall infarction. ST elevation in leads I, AVL and V2-V5. Reciprocal depressions in the inferior leads (II,III,AVF)
-
Acute MI with proximal LAD occlusion
-
A 2 weeks old anterior infarction with Q waves in V2-V4 and persisting ST elevation, a sign of formation of a cardiac aneurysm.
References
<biblio>
- Wung pmid=16777513
</biblio>