Technical Problems: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Lead reversals== | ==Lead reversals== | ||
[[Image:cableReversal1.png|thumb]] | [[Image:cableReversal1.png|thumb|Right arm lef arm lead reversal can be distinguished from the (much rarer) dextrocardia by looking at the p-wave.]] | ||
[[Image:cableReversal2.png|thumb]] | [[Image:cableReversal2.png|thumb]] | ||
Sometimes an ECG is made properly. Mistakes do happen and leads can be switched. Always remain careful to check this or you might come to the wrong conclusions. One of the most common mistakes is to switch the right and left arm. This will result in negative complexes in I, indicating a right axis deviation! | Sometimes an ECG is made properly. Mistakes do happen and leads can be switched. Always remain careful to check this or you might come to the wrong conclusions. One of the most common mistakes is to switch the right and left arm. This will result in negative complexes in I, indicating a right axis deviation! | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 18 June 2007
Lead reversals


Sometimes an ECG is made properly. Mistakes do happen and leads can be switched. Always remain careful to check this or you might come to the wrong conclusions. One of the most common mistakes is to switch the right and left arm. This will result in negative complexes in I, indicating a right axis deviation!
Common mistakes are reversal of:
- right leg and right arm:
- Hardly any signal in lead II.
- right and left arm electrodes;
- reversal of leads II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVL
- left arm and left leg:
- reversal of leads I and II
- reversal od leads aVR and aVF
- inversion of lead III
- right arm and left leg:
- inversion of laeds I, II and III
- reversal of leads aVR and aVF
It is possible to distinguish lead reversal and dextrocardia by watching the precordial leads. Dextrocardia will show an R wave inversion, wheras lead reversal will not.
Artefacts
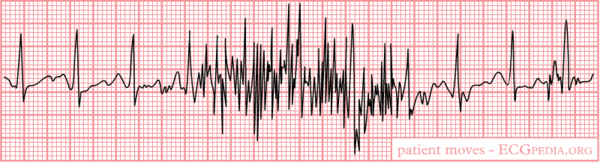




Artefacts (disturbances) can have many causes. Common causes are:
- Movement
- Electrical interference