RBBB: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
==More specific definitions== | ==More specific definitions== | ||
A more specific definition of RBBB is given by the ACC/ESC consensus document: | A more specific definition of RBBB is given by the ACC/ESC consensus document<cite>ESC-ECG</cite>: | ||
#QRS duration greater than or equal to 120 ms in adults, greater than 100 ms in children ages 4 to 16 years, and greater than 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age. | #QRS duration greater than or equal to 120 ms in adults, greater than 100 ms in children ages 4 to 16 years, and greater than 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age. | ||
Revision as of 09:20, 25 August 2012
- Criteria for right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- QRS >0,12 sec
- Slurred S wave in lead I and V6
- RSR'-pattern in V1 where R' > R
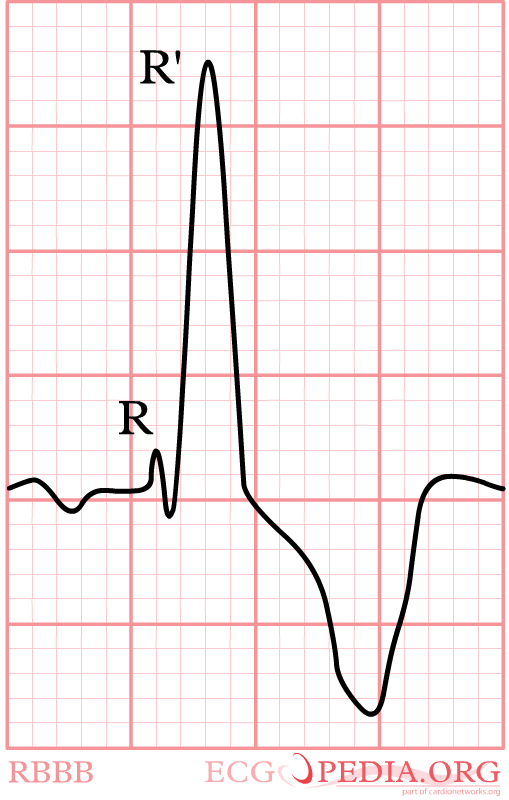

Again, watch V1. In right bundle branch block (RBBB) the conduction in the bundle to the right ventricle is slow. As the right ventricles depolarizes, the left ventricle is often halfway finished and few counteracting electrical activity is left. The last electrical activity is thus to the right, or towards lead V1. In RBBB the QRS complex in V1 is always markedly positive.
Diagnosing myocardial infarction in RBBB is not as difficult as in LBBB.
More specific definitions
A more specific definition of RBBB is given by the ACC/ESC consensus documentESC-ECG:
- QRS duration greater than or equal to 120 ms in adults, greater than 100 ms in children ages 4 to 16 years, and greater than 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age.
- rsr′, rsR′, or rSR′ in leads V1 or V2. The R′ or r′ deflection is usually wider than the initial R wave. In a minority of patients, a wide and often notched R wave pattern may be seen in lead V1 and/or V2.
- S wave of greater duration than R wave or greater than 40 ms in leads I and V6 in adults.
- Normal R peak time in leads V5 and V6 but greater than 50 ms in lead V1.
Of the above criteria, the first 3 should be present to make the diagnosis. When a pure dominant R wave with or without a notch is present in V1, criterion 4 should be satisfied.
{{{1}}}