Introduction to Arrhythmias: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
A good stepwise approach to interpret the heart rhythm is to follow these steps: | A good stepwise approach to interpret the heart rhythm is to follow these steps: | ||
*Is this my | *Is this my patient's ECG or is this an artifact? (applies especially in stressfull situations) | ||
*What is the '''ventricular [[Rate|heart rate]]'''? | *What is the '''ventricular [[Rate|heart rate]]'''? | ||
**>100 bpm = tachycardia | **>100 bpm = tachycardia | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 19 April 2011
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de jong | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
Arrhythmias (non-normal heart rhythms) can be a challenge to understand, but with a systematic approach, diagnosis is often less difficult than it may appear at first.
A good stepwise approach to interpret the heart rhythm is to follow these steps:
- Is this my patient's ECG or is this an artifact? (applies especially in stressfull situations)
- What is the ventricular heart rate?
- >100 bpm = tachycardia
- <60 bpm = bradycardia
- Are there extra beats? -> Ectopic Beats
- Cherchez le P, French for find the P waves.
- Do you see P waves? Leads II and V1 are often most suitable to find P waves.
- What is the rate of the P waves?
- What is the P wave morphology?
- What is the relationship between P waves and QRS complexes?
- Is there a 1:1 relation between P waves and QRS complexes? If not there may be AV dissociation due to a Ventricular Arrhythmias or AV block
- Is every P wave followed by a QRS complex? And every QRS preceded by a P wave?
- What is the PR interval and does it change?
- What is the QRS width?
- If the QRS < 120ms (i.e. a narrow complex), then it is either a sinus arrhythmia, supraventricular rhythm or a junctional tachycardia. In tachycardias, this flowchart will lead to the right diagnosis.ESCnarrowQRS
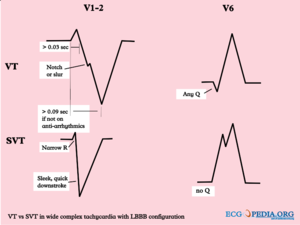
- If the QRS > 120ms it is either a ventricular tachycardia or a supraventricular rhythm with additional bundle branch block. This is a challenging diagnosis. Therefore a flowchart which incoporates the Brugada criteria for VT should be used.Brugada Another method to discriminate VT from SVT has been proposed by Vereckei et al.vereckeiIn that paper an excellent review is given on the subject by Dendi and Josephson.dendi
- What is the Heart Axis and did it change?
- If the heart axis turns significantly when compared to the heart axis during sinus rhythm a ventricular origin of the rhythm is more likely.
- What is the clinical setting?
- A wide complex tachycardia in a hemodynamically unstable 70-year-old man with previous myocardial infarction should be considered a ventricular tachycardia until proven otherwise
- A wide complex tachycardia in a 24-year-old woman with recurrent spells of tachycardia that respond to vagal maneuvers is most likely an AVNRT with aberrant conduction.
{{{1}}}