Introduction: Difference between revisions
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
Also read our '''[[Frequently Asked Questions]]''' section. | Also read our '''[[Frequently Asked Questions]]''' section. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:52, 15 March 2011
| «/ | Basics» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
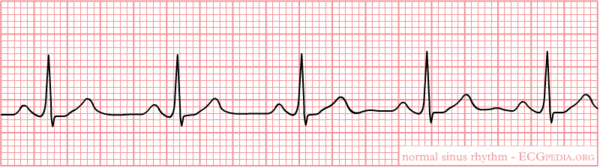
The aim of this course is to enable the student to understand and recognize normal ECGs and interpret abnormalities. The course is divided into two different sections. First the basics will be presented. This is followed by the interpretation of the normal ECG according to the 7+2 step plan:
7+2 step plan
- Step 1: Rhythm
- Step 2: Rate
- Step 3: Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT)
- Step 4: Heart axis
- Step 5: P wave morphology
- Step 6: QRS morphology
- Step 7: ST morphology
- Step 7+1: Compare the current ECG with a previous one
- Step 7+2: Conclusion
Note: It is important to realize that not all these steps may be applicable when you encounter ECG abnormalities. If, for example, the rhythm is not sinus in the first step, the algorithm to analyze arrhythmias should be followed. If a Left Bundle Branch Block is present in step 3, ST morphology will be strongly influenced by this defect.
Finally the real world is presented through practice ECGs.
After you have finished the course you are invited to come back to read more about abnormal ECGs in the ECG textbook.
ECG textbook
- Normal Tracing
- A Concise History of the ECG
- Technical Problems
- Sinus Rhythms
- Arrhythmias:
- AV Conduction
- Intraventricular Conduction
- Myocardial Infarction
- Chamber Hypertrophy
- Repolarization
- Clinical Disorders
- Electrolyte Disorders
- Pacemaker
- ECGs in Athletes
- ECGs in Children
- Accuracy of Computer Interpretation
Also read our Frequently Asked Questions section.