P Wave Morphology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|editor= | |editor= | ||
}} | }} | ||
<div style="float:left"> | |||
__TOC__ | |||
</div> | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==The Normal P wave== | |||
{{box| | |||
The '''P wave morphology''' can reveal right or left atrial hypertrophy or atrial arrhythmias and is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm. | |||
'''Characteristics of a normal p wave:'''<cite>Spodick</cite> | |||
*The maximal height of the P wave is 2.5 mm in leads II and / or III | |||
The P | *The p wave is positive in II and AVF, and biphasic in V1 | ||
*The p wave duration is shorter than 0.12 seconds | |||
}} | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
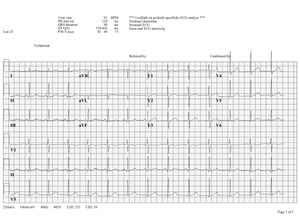
| | | |[[Image:Normaal ecg.jpg|thumb|center|300px|An example of normal sinus rhythm.]] | ||
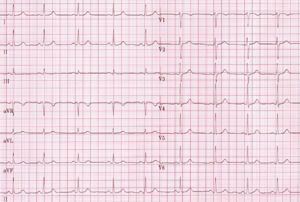
| |[[Image:Nsr.jpg|300px|thumb|center}Another example of normal sinus rhythm.]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | |||
==The Abnormal P wave== | |||
Elevation or depression of the [[PTa segment]] (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from [[Ischemia#Atrial infarction| | Elevation or depression of the [[PTa segment]] (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from [[Ischemia#Atrial infarction|atrial infarction]] or [[Clinical Disorders#Pericarditis|pericarditis]]. | ||
If the p-wave is enlarged, the [[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment#Left_atrial_enlargement|atria are enlarged]]. | If the p-wave is enlarged, the [[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment#Left_atrial_enlargement|atria are enlarged]]. | ||
If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an [[ectopic atrial rhythm]] not originating from the sinus node. | If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an [[ectopic atrial rhythm]] not originating from the sinus node. | ||
{{ | <div align="left"> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
Image: | | | ||
Image: | {| | ||
</ | |- | ||
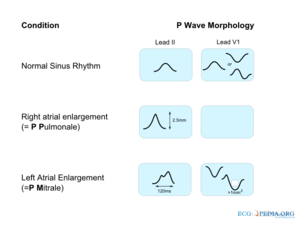
| | [[Image:p_wave_morphology.png|center|thumb|300px|Altered P wave morphology is seen in left or right atrial enlargement.]] | |||
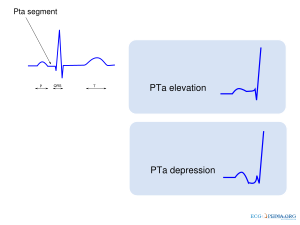
| | [[Image:pta_changes.svg|thumb|center|300px|The PTa segment can be used to diagnose pericarditis or atrial infarction.]] | |||
|} | |||
|} | |||
</div> | |||
{{box| | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#Spodick pmid=1575201 | #Spodick pmid=1575201 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
}} | |||
[[Category:ECG Course]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:39, 12 January 2011
| «Step 4:Heart axis | Step 6: QRS morphology» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD, A. Bouhiouf, Msc | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
The Normal P wave
The P wave morphology can reveal right or left atrial hypertrophy or atrial arrhythmias and is best determined in leads II and V1 during sinus rhythm.
Characteristics of a normal p wave:Spodick
- The maximal height of the P wave is 2.5 mm in leads II and / or III
- The p wave is positive in II and AVF, and biphasic in V1
- The p wave duration is shorter than 0.12 seconds
The Abnormal P wave
Elevation or depression of the PTa segment (the part between the p wave and the beginning of the QRS complex) can result from atrial infarction or pericarditis.
If the p-wave is enlarged, the atria are enlarged.
If the P wave is inverted, it is most likely an ectopic atrial rhythm not originating from the sinus node.
|
{{{1}}}