Answer MI 14: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m Answers example 2 moved to Answer MI 14 |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:Casus2_2.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 14. Click on image for enlargement.]] | [[Image:Casus2_2.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 14. Click on image for enlargement.]] | ||
[[Image:Casus2_1.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 14. | [[Image:Casus2_1.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 14. Note that V3-V6 are on the right side of the chest. Click on image for enlargement.]] | ||
V6 are on the right side of the chest. Click on image for enlargement.]] | |||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
===Answer=== | ===Answer=== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:08, 11 November 2008
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
Where is this myocardial infarction located?
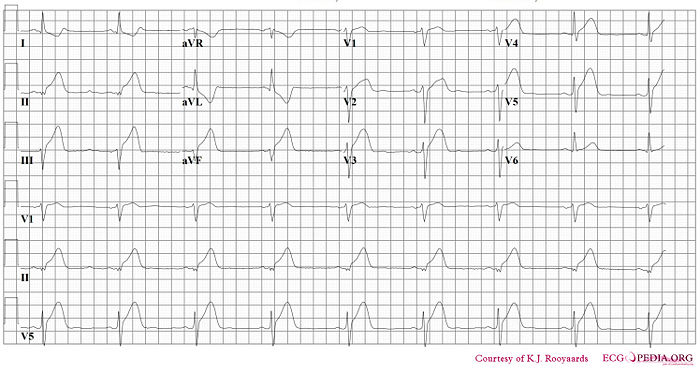
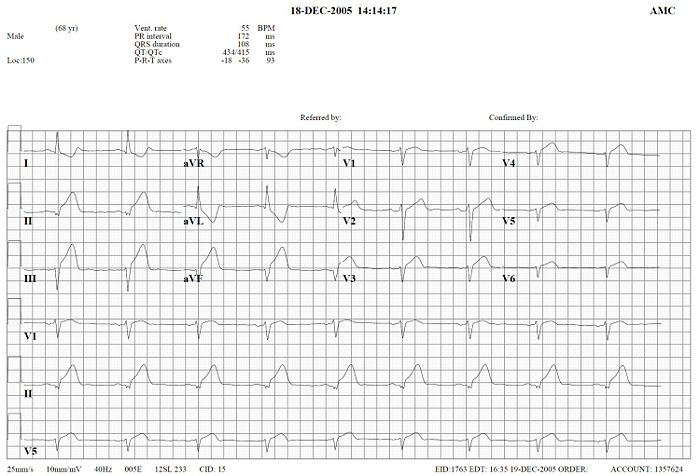
Answer
- Describe the ECG according to the 7 + 2 stepplan
- Rhythm
- This is a regular rhythm and every QRS complex is preceded by a p wave. The p wave is positive in II, III and AVF and originates form the sinusnode. Conclusion: sinusrhythm.
- Heartfrequency.
- Use the 'Countingmethod' (6 big grids ~> 300-150-100-75-60-50), so 50/min.
- Conductiontimes (PQ,QRS,QT)
- PQ-interval=0.16sec (4 small grids), QRS duration=0.10sec, QT time=460ms
- Heartaxis
- Positive in I, iso-electric in II, negative in III and AVF. So, a left axis.
- P wave morphology
- The p wave is normal shaped.
- QRS morphology
- Conduction delay right, but not enough for the complete RBBB criteria (QRS < 0.12s). Slow R-wave progression in the precordial leads.
- ST morphology
- ST elevation in II,III and AVF. Reciprocal depression in I, AVR and AVL with negative T waves. Additionally discrete elevation in V2-V5. And ST-elevation in V4R
- Compare with the old ECG (not available)
- conclusion. What is going on?
- Rhythm
Answer: Inferior wall infarct with right ventricular involvement and:
- Sinusbradycardia, probably because the sinusnodebranch, coming from the RCA is lacking perfusion.
- Left heart axis