Answer MI 4: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m New page: Culprit lesion: '''RCA''' # sinus bradycardia # about 55/min # normal conduction # intermediate (normal) axis # normal p wave morphology # tall R in V2, otherwise normal QRS morphology # ... |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Case| | |||
|previouspage= MI 3 | |||
|previousname= MI 3 | |||
|nextpage=MI 5 | |||
|nextname=MI 5 | |||
}} | |||
'''Where is this myocardial infarction located?''' | |||
[[Image:ami0004.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 4]] | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Answer== | |||
Culprit lesion: '''RCA''' | Culprit lesion: '''RCA''' | ||
Latest revision as of 09:18, 11 November 2008
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
Where is this myocardial infarction located?
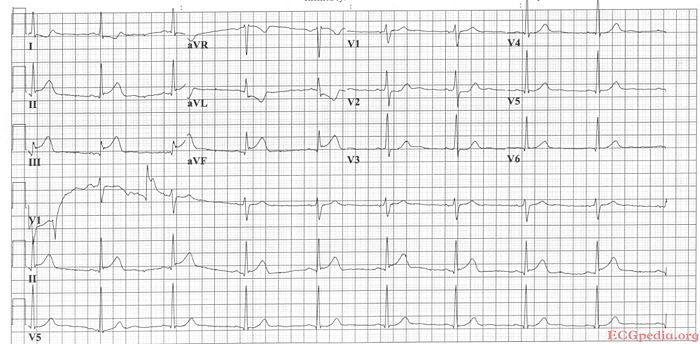
Answer
Culprit lesion: RCA
- sinus bradycardia
- about 55/min
- normal conduction
- intermediate (normal) axis
- normal p wave morphology
- tall R in V2, otherwise normal QRS morphology
- ST elevation in II, III, AVF (in III > II). Depression in I, AVL, V2.
- Conclusion: Inferoposterior MI caused by a RCA occlusion
Arguments in favor of RCA occlusion (instead of RCX):
- ST depression in I, AVL
- bradycardia
- ST elevation in III > II ('the highest ST elevation points at the culprit lesion')