Answer MI 1: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m New page: culprit laesion: '''RCX''' * sinus rythm * normal conduction intervals * normal p-waver morphology * Q in II and AVF. Tall R wave in V2-V3 * ST elevation in II, III, AVF & V5, V6. ST depre... |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Case| | |||
|previouspage= / | |||
|previousname= / | |||
|nextpage=MI 2 | |||
|nextname=MI 2 | |||
}} | |||
'''Where is this myocardial infarction located?''' | |||
[[Image:ami0001.jpg|700px|thumb|left|ECG MI 1]] | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Answer== | |||
culprit laesion: '''RCX''' | culprit laesion: '''RCX''' | ||
* sinus rythm | * sinus rythm | ||
Latest revision as of 09:07, 11 November 2008
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
Where is this myocardial infarction located?
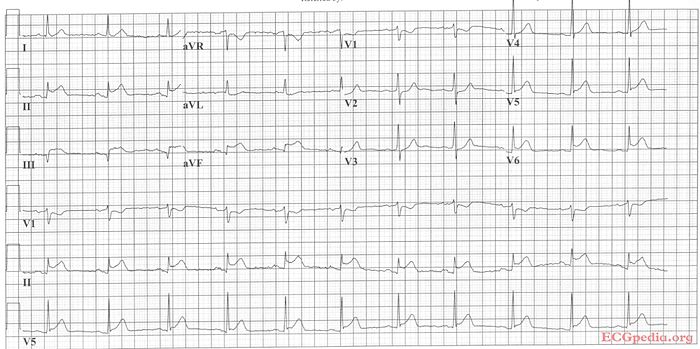
Answer
culprit laesion: RCX
- sinus rythm
- normal conduction intervals
- normal p-waver morphology
- Q in II and AVF. Tall R wave in V2-V3
- ST elevation in II, III, AVF & V5, V6. ST depression in V2.
- Conclusion: Infero- (II,III,AVF) postero- (depressions in V2-V3) lateral (V5,V6) infarct