QRS Morphology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m Reverted edits by 195.229.242.57 (Talk); changed back to last version by Drj |
m moved QRS morphology to QRS Morphology |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|nextname=Step 7: ST morphology | |nextname=Step 7: ST morphology | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{authors| | {{authors| | ||
|mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | |mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
|editor= | |editor= | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Image:Nsr.jpg|thumb|right|300px| Normal sinus rhythm with normal QRS morphology.]] | |||
The basic questions in judging QRS morphology are: | The basic questions in judging QRS morphology are: | ||
*Are there any [[Q waves|pathological Q waves]] as a sign of previous myocardial infarction? | *Are there any [[Q waves|pathological Q waves]] as a sign of previous myocardial infarction? | ||
*Are there signs of left or right ventricular [[hypertrophy]]? | *Are there signs of left or right ventricular [[hypertrophy]]? | ||
*Does the QRS complex show [[ | *Does the QRS complex show [[microvoltage]] (roughly QRS < 5mm)? | ||
*Is the conduction normal or [[Conduction delay| | *Is the conduction normal or [[Conduction delay|prolonged]] (QRS-interval > 0,12s)? | ||
*Is the R wave propagation normal? Normally R waves become larger from V1-V5. At V5 it should be maximal. If the R wave in V2 is larger than in V3, this could be a sign of a (previous) [[Posterior MI|posterior myocardial infarction]]. Other causes are noted in the chapter [[Clockwise and Counterclockwise rotation]]. | *Is the R wave propagation normal? Normally R waves become larger from V1-V5. At V5 it should be maximal. If the R wave in V2 is larger than in V3, this could be a sign of a (previous) [[Posterior MI|posterior myocardial infarction]]. Other causes are noted in the chapter [[Clockwise and Counterclockwise rotation]]. | ||
If all these items are normal you can go on to the next step: [[ST morphology]]. | If all these items are normal you can go on to the next step: [[ST morphology]]. | ||
[[Category:ECG Course]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:05, 24 January 2010
| «Step 5: P wave morphology | Step 7: ST morphology» |
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong, MD | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
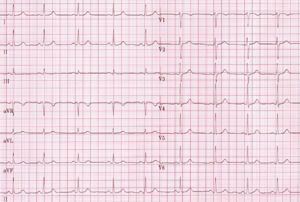
The basic questions in judging QRS morphology are:
- Are there any pathological Q waves as a sign of previous myocardial infarction?
- Are there signs of left or right ventricular hypertrophy?
- Does the QRS complex show microvoltage (roughly QRS < 5mm)?
- Is the conduction normal or prolonged (QRS-interval > 0,12s)?
- Is the R wave propagation normal? Normally R waves become larger from V1-V5. At V5 it should be maximal. If the R wave in V2 is larger than in V3, this could be a sign of a (previous) posterior myocardial infarction. Other causes are noted in the chapter Clockwise and Counterclockwise rotation.
If all these items are normal you can go on to the next step: ST morphology.