Answer DRJ case 1: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Googletrans (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Googletrans (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A. This ECG shows a severely prolonged | [[File:DVA2393.jpg|800px]] | ||
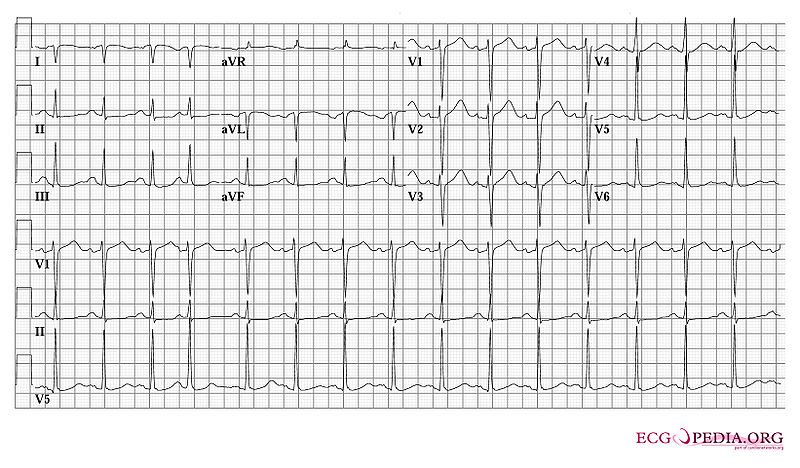
'''Question: This ECG was made shortly after this patient had been resuscitated. The patient was normothermic. What arrhythmia likely initiated the syncope? What technical abnormality is seen?''' | |||
<div style="padding-left:24px"> | |||
A. This ECG shows a severely prolonged QTc interval, which makes the patient prone to Torsade de Pointes and potential ventricular fibrillation | |||
B. Lead I has a negative P wave and Negative QRS complex. The arm leads were interchanged while recording this ECG. | |||
C. The S in v1 + the R in v5 (equaling 35mm or greater) are indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy | |||
</div> | |||
'''Answer:''' | |||
'''A:''' This ECG shows a severely prolonged QTc interval, which makes the patient prone to Torsade de Pointes and potential ventricular fibrillation | |||
Latest revision as of 09:15, 10 June 2012
Question: This ECG was made shortly after this patient had been resuscitated. The patient was normothermic. What arrhythmia likely initiated the syncope? What technical abnormality is seen?
A. This ECG shows a severely prolonged QTc interval, which makes the patient prone to Torsade de Pointes and potential ventricular fibrillation
B. Lead I has a negative P wave and Negative QRS complex. The arm leads were interchanged while recording this ECG.
C. The S in v1 + the R in v5 (equaling 35mm or greater) are indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy
Answer:
A: This ECG shows a severely prolonged QTc interval, which makes the patient prone to Torsade de Pointes and potential ventricular fibrillation