ECG in Congenital Heart Disease: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Congenital Heart Disease can result in ECG changes, often related to atrial or ventricular overload and enlargement. Below a list of relatively common forms of congenital heart disease and their potential ECG changes. Adapted from Khairy et al.<cite>khairy</cite> | |||
==Secundum atrial septal defect== | ==Secundum atrial septal defect== | ||
Information about [[w:Atrial_septal_defect|Secundum atrial septal defec on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, increased risk of AF with age | *[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, increased risk of AF with age | ||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: first degree AV block in 6-19% | *[[Conduction|PR interval]]: first degree AV block in 6-19% | ||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: 0° to 180°; RAD; LAHB | *[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: 0° to 180°; RAD; LAD in Holt-Oram or LAHB | ||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: | * QRS Configuration: rSr´ or rsR´ with RBBBi>RBBBc | ||
*Particularities: | * Atrial Enlargement: RAE 35% | ||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Uncommon | |||
*Particularities: "Crochetage" pattern | |||
==Ventricular Septal Defect== | ==Ventricular Septal Defect== | ||
Information about [[w:Ventricular_septal_defect|Ventricular Septal Defect on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal or mild ↑; 1° AVB 10% | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: RAD with BVH; LAD 3% to 15% | |||
* QRS Configuration: Normal or rsr´; possible RBBB | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE±LAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: BVH 23% to 61%; RVH with Eisenmenger | |||
*Particularities: Katz-Wachtel phenomenon | |||
==AV canal defect== | |||
Information about [[w:Atrioventricular_septal_defect|AV canal defect on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs 30% | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: 1° AVB >50% | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Moderate to extreme LAD; normal with atypical | |||
* QRS Configuration: rSr´ or rsR´ | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Uncommon in partial; BVH in complete; RVH with Eisenmenger | |||
*Particularities: Inferoposteriorly displaced AVN | |||
==Patent ductus arteriosus== | |||
Information about [[w:Patent_ductus_arteriosus|Patent ductus arteriosus on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, ↑ IART/AF with age | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: ↑ PR 10% to 20% | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Normal | |||
* QRS Configuration: Deep S V<sub>1</sub>, tall R V<sub>5</sub> and V<sub>6</sub> | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: LAE with moderate PDA | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Uncommon | |||
*Particularities: Often either clinically silent or Eisenmenger | |||
==Pulmonary stenosis== | |||
Information about [[w:Pulmonary_valve_stenosis|Pulmonary stenosis on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Normal if mild; RAD with moderate/severe | |||
* QRS Configuration: Normal; or rSr´; R´ increases with severity | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: RVH; severity correlates with R:S in V<sub>1</sub> and V<sub>6</sub> | |||
*Particularities: Axis deviation correlates with RVP | |||
==Aortic coarctation== | |||
Information about [[w:Coarctation_of_the_aorta|Aortic coarctation on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Normal or LAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Normal | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: LVH, especially by voltage criteria | |||
*Particularities: Persistent RVH rare beyond infancy | |||
==Ebstein’s anomaly== | |||
[[File:E000403.jpg|thumb|300px|ECG from a patient with Ebstein's anomaly showing huge P waves and low amplitude QRS waves. RBBB and T wave inversion are not present on this ECG.]] | |||
[[File:DVA0559.jpg|thumb|300px|ECG from a patient with Ebstein's anomaly]] | |||
Information about [[w:Ebstein's_anomaly|Ebstein's anomaly on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, possible EAR, SVT; AF/IART 40% | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: 1° AVB common; short if WPW | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Normal or LAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Low-amplitude multiphasic atypical RBBB | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: RAE with Himalayan P waves | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Diminutive RV | |||
*Particularities: Accessory pathway common; Q II, III, aVF, and V<sub>1</sub>–V<sub>4</sub> | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==Surgically repaired TOF== | |||
Information about [[w:Tetralogy_of_Fallot|Surgically repaired TOF on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs; IART 10%; VT 12% | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal or mild ↑ | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Normal or RAD; LAD 5% to 10% | |||
* QRS Configuration: RBBB 90% | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Peaked P waves; RAE possible | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: RVH possible if RVOT obstruction or PHT | |||
*Particularities: QRS duration±QTd predictive of VT/SCD | |||
==Congenitally corrected TGA== | |||
Information about [[w:Levo-Transposition_of_the_great_arteries|Congenitally corrected TGA on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: 1° AVB >50%; AVB 2%/year | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: LAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Absence septal q; Q in III, aVF, and right precordium | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Not if no associated defects | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Not if no associated defects | |||
*Particularities: Anterior AVN; positive T precordial; WPW with Ebstein’s | |||
==Complete TGA/intra-atrial baffle== | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: Sinus brady 60%; EAR; junctional; IART 25% | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: RAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Absence of q, small r, deep S in left precordium | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: RVH; diminutive LV | |||
*Particularities: Possible AVB if VSD or TV surgery | |||
==UVH with Fontan== | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: Sinus brady 15%; EAR; junctional; IART >50% | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal in TA; 1° AVB in DILV | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: LAD in single RV, TA, single LV with noninverted outlet | |||
* QRS Configuration: Variable; ↑R and S amplitudes in limb and precordial leads | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: RAE in TA | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: RVH with single RV; possible LVH with single LV | |||
*Particularities: Absent sinus node in LAI; AV block with L-loop or AVCD | |||
==Dextrocardia / Situs inversus== | |||
Information about [[w:Dextrocardia|Dextrocardia on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
[[File:Puzzle_2007_12_426_fig1.jpg|thumb|300px|An example of dextrocardia]] | |||
[[File:Situs_inversus.jpg|thumb|300px|Situs inversus]] | |||
[[File:Situs_inversus_mirrored_lead_positioning.jpg|thumb|300px|Dextrocardia with mirrored lead positioning]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm, P-wave axis 105° to 165° with situs inversus | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: RAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Inverse depolarization and repolarization | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Not with situs inversus | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: LVH: tall R V<sub>1</sub>–V<sub>2</sub>; RVH: deep Q, small R V<sub>1</sub> and tall R right lateral | |||
*Particularities: Situs solitus: normal P-wave axis and severe CHD | |||
{{clr}} | |||
==ALCAPA== | |||
Information about [[w:Anomalous_Left_Coronary_Artery_From_the_Pulmonary_Artery|ALCAPA on Wikipedia (external link)]] | |||
*[[Rhythm]]: normal sinus rhythm | |||
*[[Conduction|PR interval]]: Normal | |||
*[[Heart axis|QRS axis]]: Possible LAD | |||
* QRS Configuration: Ant-lat Q waves; possible ant-sept Q waves | |||
* Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE | |||
*[[Chamber_Hypertrophy_and_Enlargment|Ventricular hypertrophy]]: Selective hypertrophy of posterobasal LV | |||
*Particularities: Possible ischemia | |||
==References== | |||
<biblio> | |||
#khairy pmid=18056539 | |||
</biblio> | |||
Latest revision as of 18:55, 24 April 2013
Congenital Heart Disease can result in ECG changes, often related to atrial or ventricular overload and enlargement. Below a list of relatively common forms of congenital heart disease and their potential ECG changes. Adapted from Khairy et al.khairy
Secundum atrial septal defect
Information about Secundum atrial septal defec on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, increased risk of AF with age
- PR interval: first degree AV block in 6-19%
- QRS axis: 0° to 180°; RAD; LAD in Holt-Oram or LAHB
- QRS Configuration: rSr´ or rsR´ with RBBBi>RBBBc
- Atrial Enlargement: RAE 35%
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Uncommon
- Particularities: "Crochetage" pattern
Ventricular Septal Defect
Information about Ventricular Septal Defect on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs
- PR interval: Normal or mild ↑; 1° AVB 10%
- QRS axis: RAD with BVH; LAD 3% to 15%
- QRS Configuration: Normal or rsr´; possible RBBB
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE±LAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: BVH 23% to 61%; RVH with Eisenmenger
- Particularities: Katz-Wachtel phenomenon
AV canal defect
Information about AV canal defect on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs 30%
- PR interval: 1° AVB >50%
- QRS axis: Moderate to extreme LAD; normal with atypical
- QRS Configuration: rSr´ or rsR´
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Uncommon in partial; BVH in complete; RVH with Eisenmenger
- Particularities: Inferoposteriorly displaced AVN
Patent ductus arteriosus
Information about Patent ductus arteriosus on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, ↑ IART/AF with age
- PR interval: ↑ PR 10% to 20%
- QRS axis: Normal
- QRS Configuration: Deep S V1, tall R V5 and V6
- Atrial Enlargement: LAE with moderate PDA
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Uncommon
- Particularities: Often either clinically silent or Eisenmenger
Pulmonary stenosis
Information about Pulmonary stenosis on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval: Normal
- QRS axis: Normal if mild; RAD with moderate/severe
- QRS Configuration: Normal; or rSr´; R´ increases with severity
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: RVH; severity correlates with R:S in V1 and V6
- Particularities: Axis deviation correlates with RVP
Aortic coarctation
Information about Aortic coarctation on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval: Normal
- QRS axis: Normal or LAD
- QRS Configuration: Normal
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: LVH, especially by voltage criteria
- Particularities: Persistent RVH rare beyond infancy
Ebstein’s anomaly
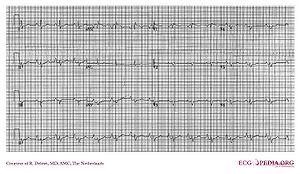
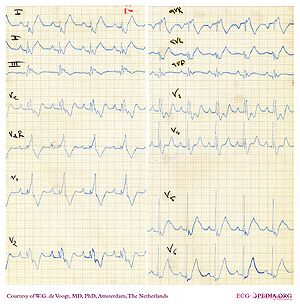
Information about Ebstein's anomaly on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, possible EAR, SVT; AF/IART 40%
- PR interval: 1° AVB common; short if WPW
- QRS axis: Normal or LAD
- QRS Configuration: Low-amplitude multiphasic atypical RBBB
- Atrial Enlargement: RAE with Himalayan P waves
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Diminutive RV
- Particularities: Accessory pathway common; Q II, III, aVF, and V1–V4
Surgically repaired TOF
Information about Surgically repaired TOF on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, PVCs; IART 10%; VT 12%
- PR interval: Normal or mild ↑
- QRS axis: Normal or RAD; LAD 5% to 10%
- QRS Configuration: RBBB 90%
- Atrial Enlargement: Peaked P waves; RAE possible
- Ventricular hypertrophy: RVH possible if RVOT obstruction or PHT
- Particularities: QRS duration±QTd predictive of VT/SCD
Congenitally corrected TGA
Information about Congenitally corrected TGA on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval: 1° AVB >50%; AVB 2%/year
- QRS axis: LAD
- QRS Configuration: Absence septal q; Q in III, aVF, and right precordium
- Atrial Enlargement: Not if no associated defects
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Not if no associated defects
- Particularities: Anterior AVN; positive T precordial; WPW with Ebstein’s
Complete TGA/intra-atrial baffle
- Rhythm: Sinus brady 60%; EAR; junctional; IART 25%
- PR interval: Normal
- QRS axis: RAD
- QRS Configuration: Absence of q, small r, deep S in left precordium
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible RAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: RVH; diminutive LV
- Particularities: Possible AVB if VSD or TV surgery
UVH with Fontan
- Rhythm: Sinus brady 15%; EAR; junctional; IART >50%
- PR interval: Normal in TA; 1° AVB in DILV
- QRS axis: LAD in single RV, TA, single LV with noninverted outlet
- QRS Configuration: Variable; ↑R and S amplitudes in limb and precordial leads
- Atrial Enlargement: RAE in TA
- Ventricular hypertrophy: RVH with single RV; possible LVH with single LV
- Particularities: Absent sinus node in LAI; AV block with L-loop or AVCD
Dextrocardia / Situs inversus
Information about Dextrocardia on Wikipedia (external link)
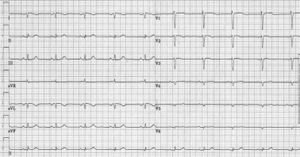
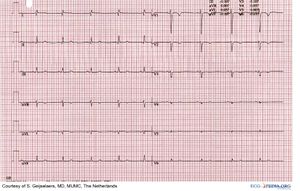
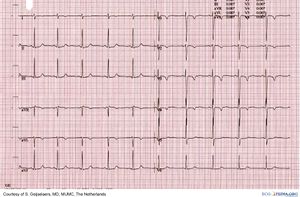
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm, P-wave axis 105° to 165° with situs inversus
- PR interval: Normal
- QRS axis: RAD
- QRS Configuration: Inverse depolarization and repolarization
- Atrial Enlargement: Not with situs inversus
- Ventricular hypertrophy: LVH: tall R V1–V2; RVH: deep Q, small R V1 and tall R right lateral
- Particularities: Situs solitus: normal P-wave axis and severe CHD
ALCAPA
Information about ALCAPA on Wikipedia (external link)
- Rhythm: normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval: Normal
- QRS axis: Possible LAD
- QRS Configuration: Ant-lat Q waves; possible ant-sept Q waves
- Atrial Enlargement: Possible LAE
- Ventricular hypertrophy: Selective hypertrophy of posterobasal LV
- Particularities: Possible ischemia
References
<biblio>
- khairy pmid=18056539
</biblio>