Pulmonary Embolism: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In case of a [[w:Pulmonary_embolism|pulmonary embolism]] several clinical features may be present:<cite>Rodger</cite> | In case of a [[w:Pulmonary_embolism|pulmonary embolism]] several clinical features may be present:<cite>Rodger</cite> | ||
* [[Sinus Tachycardia]] | * [[Sinus Tachycardia]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 5: | ||
**[[Heartaxis]] is to the right | **[[Heartaxis]] is to the right | ||
**[[RBBB|Right bundle branch block (RBBB)]] | **[[RBBB|Right bundle branch block (RBBB)]] | ||
"S1Q3T3" | |||
* Deep S in I | * Deep S in I | ||
* Q and negative T in III | * Q and negative T in III | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
Pulmonary embolism cannot solely be diagnosed using an ECG, but it may be helpful. | Pulmonary embolism cannot solely be diagnosed using an ECG, but it may be helpful. | ||
<gallery> | |||
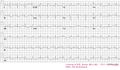
Image:Pulm_embolism.jpg|ECG of a patiënt with pulmonary embolism | |||
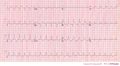
Image:pulm_embolism_ecg2.jpg|Another example of an ECG of a patiënt with pulmonary embolism. Note the tachycardia and right axis. | |||
File:E000004.jpg|An example of right ventricular hypertrophy (and right atrial enlargement) in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation. | |||
File:E0003193.png|A 12 lead ECG of a patient with pulmonary embolism | |||
</gallery> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#Rodger pmid=11018210 | #Rodger pmid=11018210 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:11, 19 December 2012
In case of a pulmonary embolism several clinical features may be present:Rodger
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Stress on the right ventricle:
- right atrial dilatation
- Heartaxis is to the right
- Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
"S1Q3T3"
- Deep S in I
- Q and negative T in III
- T wave inversion anterior Ferrari
Pulmonary embolism cannot solely be diagnosed using an ECG, but it may be helpful.
-
ECG of a patiënt with pulmonary embolism
-
Another example of an ECG of a patiënt with pulmonary embolism. Note the tachycardia and right axis.
-
An example of right ventricular hypertrophy (and right atrial enlargement) in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation.
-
A 12 lead ECG of a patient with pulmonary embolism
References
<biblio>
- Rodger pmid=11018210
</biblio>