RBBB: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Reverted edits by 222.62.198.66 (Talk); changed back to last version by Drj) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:RBBB.png|thumb| Right bundle branch block (RBBB) in lead V1]] | [[Image:RBBB.png|thumb| Right bundle branch block (RBBB) in lead V1]] | ||
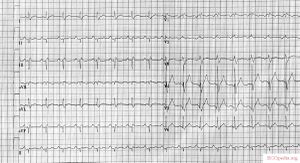
[[Image:ECG_RBTB_LAtrD.jpg|thumb| A 12 lead ECG with right bundle branch block (and [[P wave morphology|left atrial enlargement]])]] | [[Image:ECG_RBTB_LAtrD.jpg|thumb| A 12 lead ECG with right bundle branch block, left axis (LAFB)(and [[P wave morphology|left atrial enlargement]])]] | ||
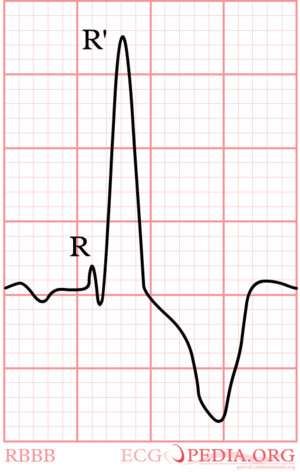
;Criteria for right bundle branch block (RBBB) <cite>Garcia</cite> | ;Criteria for right bundle branch block (RBBB) <cite>Garcia</cite> | ||
:QRS >0,12 sec | :QRS >0,12 sec | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 4 December 2007

A 12 lead ECG with right bundle branch block, left axis (LAFB)(and left atrial enlargement)
- Criteria for right bundle branch block (RBBB) [1]
- QRS >0,12 sec
- Slurred S wave in lead I and V6
- RSR'-pattern in V1 where R' > R
Again, watch V1. In right bundle branch block (RBBB) the conduction in the bundle to the right ventricle is slow. As the right ventricles depolarizes, the left ventricle is often halfway finished and few counteracting electrical activity is left. The last electrical activity is thus to the right, or towards lead V1. In RBBB the QRS complex in V1 is allways markedly positive.
Diagnosing myocardial infarction in RBBB is not as difficult as in LBBB.