Pathologic Q Waves: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
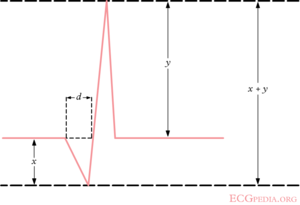
[[Image:PathoQMeasure.png|thumb| A pathological is Een pathologische golf (''x'') is dieper dan 1/3 van de hoogte van het QRS complex (''x+y'') en breder (''d'') dan 0,04 sec.]] | [[Image:PathoQMeasure.png|thumb| A pathological is Een pathologische golf (''x'') is dieper dan 1/3 van de hoogte van het QRS complex (''x+y'') en breder (''d'') dan 0,04 sec.]] | ||
[[Image:PathoQ.png|thumb| Een pathologische Q golf]] | [[Image:PathoQ.png|thumb| Een pathologische Q golf]] | ||
Pathologic Q waves are a sign of absence of electrical activity. They can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole'. Myocardial infarction results in scar tissue that is electrically dead and therefore results in pathologic Q waves. | |||
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.<cite>Alpert</cite> | |||
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated | |||
;Definition of a pathologic Q wave: | ;Definition of a pathologic Q wave: | ||
:Any Q wave in leads V1-V3 | :Any Q wave in leads V1-V3 | ||
:Q wave > or = to 30ms (0.03s) in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, V4, V4, or V6 (the Q wave changes must be present in any two contiguous lead, and be > or = 1mm in depth). | :Q wave > or = to 30ms (0.03s) in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, V4, V4, or V6 (the Q wave changes must be present in any two contiguous lead, and be > or = 1mm in depth). | ||
'''Note''': Absence of pathologic Q waves does not exclude a myocardial infarction! | |||
For those interested: the [http://www.epi.umn.edu/ecg/mncode.pdf Minnesota Code Classification System for Electrocardiographic Findings] contains a very extensive definition of pathologic Q waves. | |||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 24 July 2007
Criteria for a previous myocardial infarction
Pathologic Q waves are a sign of absence of electrical activity. They can be thought of as an elecrical 'hole'. Myocardial infarction results in scar tissue that is electrically dead and therefore results in pathologic Q waves.
The precise criteria for pathologic Q waves have been debated. Here we present the latest definition as accepted by the ESC and ACC.[1]
- Definition of a pathologic Q wave
- Any Q wave in leads V1-V3
- Q wave > or = to 30ms (0.03s) in leads I, II, aVL, aVF, V4, V4, or V6 (the Q wave changes must be present in any two contiguous lead, and be > or = 1mm in depth).
Note: Absence of pathologic Q waves does not exclude a myocardial infarction!
For those interested: the Minnesota Code Classification System for Electrocardiographic Findings contains a very extensive definition of pathologic Q waves.
Referenties
- Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, and Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined--a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000 Sep;36(3):959-69. DOI:10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00804-4 |