Ventricular Premature Beats: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chapter|Ventricular Arrhythmias}} | {{Chapter|Ventricular Arrhythmias}} | ||
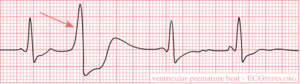
[[Image:Rhythm_ventricular_premature.png|thumb| The arrow indicates a ventricular extrasystole (VES).]] | [[Image:Rhythm_ventricular_premature.png|thumb| The arrow indicates a ventricular extrasystole (VES).]] | ||
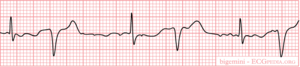
[[Image:Rhythm_bigemini.png|thumb|Bigemini: every sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole]] | |||
A VPB is an [[Ectopic Beats|ectopic beat]] that origins from the ventricles. VPBs are hardly conducted by the specialised conduction system and therefore are broad. The QRS width is at least > 0.12 seconds, but often very broad at around 0.16-0.20 seconds. | A VPB is an [[Ectopic Beats|ectopic beat]] that origins from the ventricles. VPBs are hardly conducted by the specialised conduction system and therefore are broad. The QRS width is at least > 0.12 seconds, but often very broad at around 0.16-0.20 seconds. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
*'''monomorphic''': all VPBs have the same configuration and thus have a mutual focus of origin. | *'''monomorphic''': all VPBs have the same configuration and thus have a mutual focus of origin. | ||
*'''multiformic''': the complexes have different configurations. | *'''multiformic''': the complexes have different configurations. | ||
*'''Bigemini''': every sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole. | |||
*'''Trigemini''': every second sinus beat is follow by a ventricular extrasystole. | |||
Three or more consecutive VPBs (but in total of no more than 30 seconds duration) are called a non-sustained [[Ventricular Tachycardia|ventricular tachycardia]]. | Three or more consecutive VPBs (but in total of no more than 30 seconds duration) are called a non-sustained [[Ventricular Tachycardia|ventricular tachycardia]]. | ||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Revision as of 15:26, 23 July 2007
| This is part of: Ventricular Arrhythmias |
A VPB is an ectopic beat that origins from the ventricles. VPBs are hardly conducted by the specialised conduction system and therefore are broad. The QRS width is at least > 0.12 seconds, but often very broad at around 0.16-0.20 seconds.
Causes: e.g. ischemia, hypoxia, old scar tissue, idiopathic. 50% of healthy men have sporadic VPBs. The origin of the VPB can be derived from its form. A LBTB-configured VPB originates in the right ventricle. A RBTB-configured VPB comes from the left ventricle. The QRS duration of a VPB is > 0.12 seconds and can be as wide as 0.16-0.20 seconds.
A sequence of three or more extrasystoles is called a non-sustained ventricular tachycardia.
If more than one VPB is present on the ECG, they can be:
- monomorphic: all VPBs have the same configuration and thus have a mutual focus of origin.
- multiformic: the complexes have different configurations.
- Bigemini: every sinus beat is followed by a ventricular extrasystole.
- Trigemini: every second sinus beat is follow by a ventricular extrasystole.
Three or more consecutive VPBs (but in total of no more than 30 seconds duration) are called a non-sustained ventricular tachycardia.