Atrial Rhythm: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chapter | {{Chapter|Supraventricular Rhythms}} | ||
{{Arrhythmias| | {{Arrhythmias| | ||
| name = Atrial Rhythm | | name = Atrial Rhythm | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}} | }} | ||
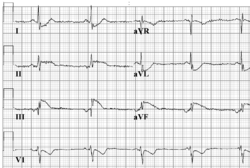
Atrial rhythm resembles sinusrhythm, but origins from a different atrial focus. It can be recognised by the abnormal configuration of the p-wave. Often the p-wave is negative in AVF, as is seen in the example. | Atrial rhythm resembles sinusrhythm, but origins from a different atrial focus. It can be recognised by the abnormal configuration of the p-wave. Often the p-wave is negative in AVF, as is seen in the example. | ||
[[File:E0003196.png|thumb|Conversion of sinus bradycardia to atrial rhythm is sometimes seen in young patients with sinus bradycardia, as in this example.]] | |||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
Latest revision as of 06:04, 19 December 2012
| This is part of: Supraventricular Rhythms |
Atrial rhythm resembles sinusrhythm, but origins from a different atrial focus. It can be recognised by the abnormal configuration of the p-wave. Often the p-wave is negative in AVF, as is seen in the example.