AV-dissociation: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(spelling fix) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
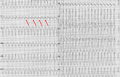
During | During A-V dissociation there is no link between the atrial and ventricular activity. A good example is Complete A-V block in which the atria can have [[sinus rhythm]] and the ventricles a [[ventricular escape rhythm]]. | ||
A-V dissociation, when observed, can be very helpful in the diagnosis of [[ventricular tachycardia]]. As a wide complex tachcyardia with AV dissociation is always a ventricular tachycardia. Sometimes, during ventricular tachycardia, the atria are activated retrogradely. Thus, A-V dissociation is not always present in ventricular tachycardia. | |||
==Voorbeelden== | ==Voorbeelden== | ||
Latest revision as of 01:21, 4 June 2012
During A-V dissociation there is no link between the atrial and ventricular activity. A good example is Complete A-V block in which the atria can have sinus rhythm and the ventricles a ventricular escape rhythm.
A-V dissociation, when observed, can be very helpful in the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia. As a wide complex tachcyardia with AV dissociation is always a ventricular tachycardia. Sometimes, during ventricular tachycardia, the atria are activated retrogradely. Thus, A-V dissociation is not always present in ventricular tachycardia.