Sino-atrial exit block: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Chapter|Sinus node rhythms and arrhythmias}} | {{Chapter|Sinus node rhythms and arrhythmias}} | ||
[[Image:sa_exit_blok.jpg|thumb|Sino-atrial exit block (more precisely: type II second degree SA exit block)]] | [[Image:sa_exit_blok.jpg|thumb|Sino-atrial exit block (more precisely: type II second degree SA exit block)]] | ||
During sino-atrial exit block, the depolarizations that occur in the sinus node cannot leave the node towards the atria. They are blocked. On the ECG this is expressed as a pause. SA exit block can be | [[Image:sa_exit_blok2.png|thumb|Sino-atrial exit block]] | ||
[[Image:sa_exit_blok3.jpg|thumb|Sino-atrial exit block]] | |||
During sino-atrial exit block, the depolarizations that occur in the sinus node cannot leave the node towards the atria. They are blocked. On the ECG this is expressed as a pause. SA exit block can be distinguished from [[sinusarrest]] because the pause in SA exit block is a multiple of the P-P interval that preceded the pause. | |||
Three subtypes can be destinguished:<cite>Braunwald</cite> | Three subtypes can be destinguished:<cite>Braunwald</cite> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:41, 21 September 2011
| This is part of: Sinus node rhythms and arrhythmias |

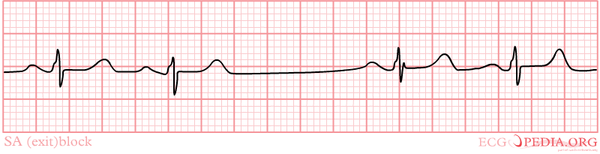

During sino-atrial exit block, the depolarizations that occur in the sinus node cannot leave the node towards the atria. They are blocked. On the ECG this is expressed as a pause. SA exit block can be distinguished from sinusarrest because the pause in SA exit block is a multiple of the P-P interval that preceded the pause.
Three subtypes can be destinguished:Braunwald
- Type I second degree (Wenkebach) SA exit block: the P-P interval progressively shortens prior to the pause
- Type II second degree SA exit block: the pause equals approximately 2-4 times the preceding PP interval
- Third degree SA exit block: absence of P waves (can only be diagnosed with an sinus node electrode, during electrophysiological evaluation)
References
<biblio>
- Braunwald isbn=0721605095
</biblio>