MI Diagnosis in LBBB or paced rhythm: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Image:E000003.jpg|Case 3: Acute MI in a patient with LBBB | Image:E000003.jpg|Case 3: Acute MI in a patient with LBBB | ||
Image:E000002.jpg|Case 3: Non-ischemic ECG in this patient | Image:E000002.jpg|Case 3: Non-ischemic ECG in this patient | ||
Image:E000406.jpg | Image:E000406.jpg|Myocardial infarction in a pacemaker patient. The ECG shows LBBB as expected during pacing, however overt repolarization abnormalities are present. | ||
Image:E000405.jpg | Image:E000405.jpg|Myocardial infarction post primary PCI in a pacemaker patient | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 28 February 2011

In case of a left bundle branch block (LBBB), infarct diagnosis based on the ECG is difficult. The baseline ST segments and T waves tend to be shifted in a discordant direction with LBBB, which can mask or mimic acute myocardial infarction. However, serial ECGs may show a moving ST segment during ischemia secondary to dynamic supply versus demand characteristics. A new LBBB is always pathological and can be a sign of myocardial infarction. The criteria (Sgarbossa LBTB) that can be used in case of a LBBB and suspicion of infarction are:
- ST elevation > 1mm in leads with a positive QRS complex (concordance in ST deviation) (score 5)
- ST depression > 1 mm in V1-V3 (concordance in ST deviation) (score 3)
- ST elevation > 5 mm in leads with a negative QRS complex (inappropriate discordance in ST deviation) (score 2). This criterium is sensitive, but not specific for ischemia in LBBB. It is however associated with a worse prognosis, when present in LBBB during ischemia.Wong
At a score-sum of 3, these criteria have a specificity of 90% for detecting a myocardial infarction.
Examples
-
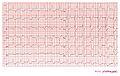
Case 1: Acute myocardial infarction in in a patient with a pacemaker and LBBB. Concordant ST elevation in V5-V6 are clearly visible. There is discordant ST segment elevation > 5 mm in lead V3.
-
Case 1: The same patient as in the first example 2 months before the myocardial infarction. Normal LBBB pattern.
-
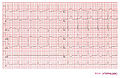
Case 2: Acute MI in a patient with LBBB
-
Case 3: Acute MI in a patient with LBBB
-
Case 3: Non-ischemic ECG in this patient
-
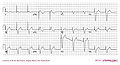
Myocardial infarction in a pacemaker patient. The ECG shows LBBB as expected during pacing, however overt repolarization abnormalities are present.
-
Myocardial infarction post primary PCI in a pacemaker patient
References
<biblio>
- LBTB pmid=8559200
- Wong pmid=15992631
</biblio>