Sick Sinus Syndrome: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
m (Undo revision 10309 by 98.243.192.55 (talk)) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
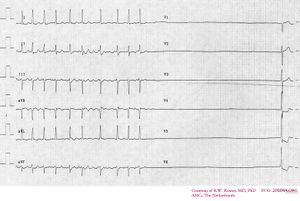
[[Image:SSS_ecg_001.jpg|thumb|ECG with Sick Sinus Syndrome. Rapid atrial fibrillation abruptly stops.]] | [[Image:SSS_ecg_001.jpg|thumb|ECG with Sick Sinus Syndrome. Rapid atrial fibrillation abruptly stops.]] | ||
In sick sinus syndrome there is a malfunctioning sinus node. Several arrhythmias can result from this: | In sick sinus syndrome there is a malfunctioning sinus node. Several arrhythmias can result from this: | ||
* Symptomatic slow [[ | * Symptomatic slow [[sinusbradycardia]] in the absence of medication | ||
* [[ | * [[Sinusarrest]] or exit block | ||
* Combinations of sinoatrial and atrioventricular | * Combinations of sinoatrial and atrioventricular conductions disturbances | ||
* Brady-tachycardia syndrome; typically there is | * Brady-tachycardia syndrome; typically there is sinusbradycardia, sinusarrest or SA-block which is alternated by periods with fast or (ir)regular atrial arrhythmias ([[Atrial Fibrillation|atrial fibrillation]], [[Atrial Flutter|atrial flutter]], [[Atrial Tachycardia|atrial tachyardia]] or [[sinustachycardia]]). | ||
Usually a [[pacemaker]] is implanted to prevent bradycardia and tachycardias are 'topped off' with anti-arrhythmics, such as beta blockers. | Usually a [[pacemaker]] is implanted to prevent bradycardia and tachycardias are 'topped off' with anti-arrhythmics, such as beta blockers. | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 25 April 2010
| This is part of: Sinus node rhythms and arrhythmias |
In sick sinus syndrome there is a malfunctioning sinus node. Several arrhythmias can result from this:
- Symptomatic slow sinusbradycardia in the absence of medication
- Sinusarrest or exit block
- Combinations of sinoatrial and atrioventricular conductions disturbances
- Brady-tachycardia syndrome; typically there is sinusbradycardia, sinusarrest or SA-block which is alternated by periods with fast or (ir)regular atrial arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachyardia or sinustachycardia).
Usually a pacemaker is implanted to prevent bradycardia and tachycardias are 'topped off' with anti-arrhythmics, such as beta blockers.