Answer MI 16
| This page is part of Cases and Examples |
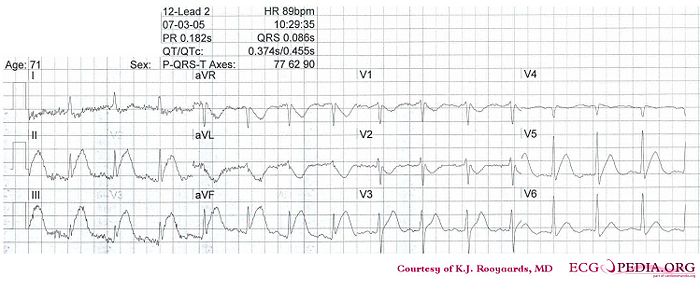
Where is this myocardial infarction located?
Answer
- Following the 7+2 steps:
- Rhythm
- This is a regular rhythm and every QRS complex is preceded by a p wave. The p wave is positive in II,III, and AVF and thus originates from the sinus node. Conclusion: sinus rhythm.
- Hartfrequency
- Use the 'count the squares' method (a bit less than 3 large squares ~> 300-150-100), thus about 90 bpm.
- Conduction (PQ,QRS,QT)
- PQ-interval=0.16sec (4 small squares), QRS duration=0.10sec, QT interval=360ms
- Hartaxis
- Positive in I, II, III, and AVF. Thus a normal heart axis.
- P wave morphology
- The p wave is difficult to assess, because of the (electrical) interference, but does not seem fulfill the criteria for left or right atrial dilatation.
- QRS morphology
- No pathologic Q waves. QRS duration < 0.12 seconds thus no bundle branch block is present. No left ventricular hypertrofy: S in V1 + R in V5 < 35mm.
- ST morphology
- Evident ST elevation in II,III, and AVF and also in V5. ST-depression in AVL and V1-V2.
- Compare with the old ECG (not available, so skip this step)
- Conclusion?
- Rhythm
Acuut Inferior-Posterior Myocardial Infarction