ICD: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Picture_ICD.jpg|thumb|An ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device)]] | [[Image:Picture_ICD.jpg|thumb|An ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device)]] | ||
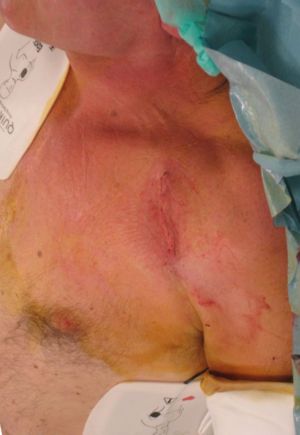
[[Image: | [[Image:ICD_wound.jpg|thumb|An ICD is usually implanted subcutaneously]] | ||
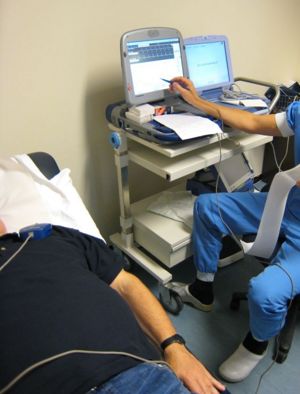
[[Image:ICD_readout.jpg|thumb|The information stored in the ICD's memory can be read out using a coil that is put on the patients clothing near the ICD. Stored information includes battery life remaining and ICD shocks]] | [[Image:ICD_readout.jpg|thumb|The information stored in the ICD's memory can be read out using a coil that is put on the patients clothing near the ICD. Stored information includes battery life remaining and ICD shocks]] | ||
ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device): this device can detect and treat [[ | ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device): this device can detect and treat [[Ventricular Tachycardia]] and [[Ventricular Fibrillation]]. Usually the first treatment is anti-tachy pacing (pacing at a rate +- 10% above the ventricular rate in ventricular tachycardia, which can convert the rhythm to sinus rhythm). If this is not effective an defibrillator shock is delivered, usually with 16-36 Joules of energy. ICDs can save lives in patients who have a high risk of ventricular arrhythmias. All ICDs have optional pacemaker activity to treat bradycardias. New biventricular ICDs have 3 leads: an atrial lead, a left ventricular lead and a right ventricular lead. | ||
Revision as of 20:04, 24 July 2007
ICD (Internal Cardioversion Device): this device can detect and treat Ventricular Tachycardia and Ventricular Fibrillation. Usually the first treatment is anti-tachy pacing (pacing at a rate +- 10% above the ventricular rate in ventricular tachycardia, which can convert the rhythm to sinus rhythm). If this is not effective an defibrillator shock is delivered, usually with 16-36 Joules of energy. ICDs can save lives in patients who have a high risk of ventricular arrhythmias. All ICDs have optional pacemaker activity to treat bradycardias. New biventricular ICDs have 3 leads: an atrial lead, a left ventricular lead and a right ventricular lead.