Ventricular Flutter
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| This is part of: Ventricular Arrhythmias |
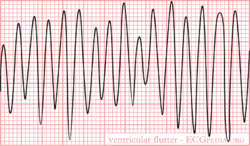
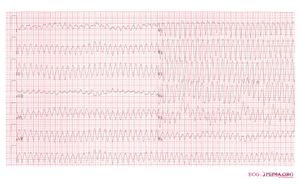
Ventricular Flutter is mostly caused by re-entry with a frequency of 300 bpm. The ECG shows a typical sinusoidal pattern. During ventricular flutter the ventricles depolarize in a circular pattern, which prevents good function. Most often this results in a minimal cardiac output and subsequent ischemia. Often deteriorates into Ventricular Fibrillation.