Sinus Node Rhythms and Arrhythmias: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
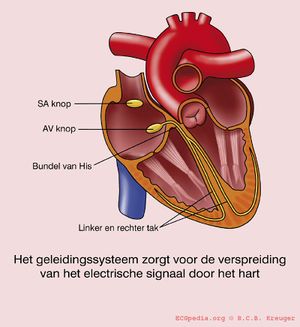
[[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb|Het geleidingssysteem zorgt voor de verspreiding van het electrisch signaal door het hart. Het normale hartritme begint in de sinusknoop en gaat dan via de AV (atrio-ventriculaire) knoop naar de bundel van His, waarna het zich splitst via de linker en rechter bundeltak.]] | [[Image:geleidingssysteem.jpg|thumb|Het geleidingssysteem zorgt voor de verspreiding van het electrisch signaal door het hart. Het normale hartritme begint in de sinusknoop en gaat dan via de AV (atrio-ventriculaire) knoop naar de bundel van His, waarna het zich splitst via de linker en rechter bundeltak.]] | ||
This part is about the normal ECG. The normal heart rhythm is sinal rhythm. That means that the rhythm has its origin in the sinal node, the heart's fastest physiological impulse generator. | |||
The sinus node (SA) is located in the upper part of the wall of the right atrium. When the sinus node generates an electrical signal, first the cells of the right atrium depolarise, then the cells of the left atrium, the AV (atrioventricular) node follows and at last the ventricles are stimulated via the His bundle. | |||
With this knowledge it is quite simple to recognise sinus rhythm on the ECG. | |||
{{clr}} | {{clr}} | ||
=== | ===The properties of normal sinus rhythm (see also [[Basics]]):=== | ||
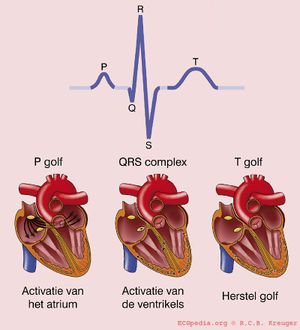
[[Image:QRSverklaring.jpg|thumb| Bij normaal sinusritme volgt na iedere atriale contractie (p-top) volgt een ventriculaire contractie (QRS complex).]] | [[Image:QRSverklaring.jpg|thumb| Bij normaal sinusritme volgt na iedere atriale contractie (p-top) volgt een ventriculaire contractie (QRS complex).]] | ||
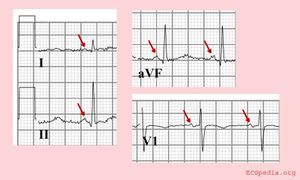
[[Image:normalSR.jpg|thumb|Normaal sinusritme met een positieve P-top in I,II en AVF én een bifasische p-top in V1.]] | [[Image:normalSR.jpg|thumb|Normaal sinusritme met een positieve P-top in I,II en AVF én een bifasische p-top in V1.]] | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 13 October 2006
This part is about the normal ECG. The normal heart rhythm is sinal rhythm. That means that the rhythm has its origin in the sinal node, the heart's fastest physiological impulse generator.
The sinus node (SA) is located in the upper part of the wall of the right atrium. When the sinus node generates an electrical signal, first the cells of the right atrium depolarise, then the cells of the left atrium, the AV (atrioventricular) node follows and at last the ventricles are stimulated via the His bundle.
With this knowledge it is quite simple to recognise sinus rhythm on the ECG.
The properties of normal sinus rhythm (see also Basics):
- Een p top (boezemcontractie) gaat vooraf aan het QRS complex
- Op iedere p top volgt een QRS complex
- Het ritme is regelmatig, maar varieert licht met de ademhaling
- De frequentie ligt tussen de 60 en 100 / minuut.
- De maximale hoogte van de p top is 2,5 mm in II en / of III
- De p top is positief in I en II, en bifasisch in V1
Deze laatste twee definities komen aan bod in het hoofdstukje p top morfologie.
Hartritmes die geen sinusritme zijn komen aan bod in het hoofdstuk ritmestoornissen.