Puzzle 2007 03 114 Answer
| Author(s) | A.A.M. Wilde, N.A. Blom | |
| NHJ edition: | 2007:03,114 | |
| These Rhythm Puzzles have been published in the Netherlands Heart Journal and are reproduced here under the prevailing creative commons license with permission from the publisher, Bohn Stafleu Van Loghum. | ||
| The ECG can be enlarged twice by clicking on the image and it's first enlargement | ||
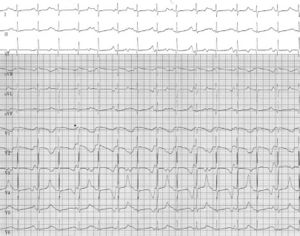
A boy with a birth weight of 3.030 g was born by caesarean section at 33 weeks of gestation because of bradycardia and severe foetal hydrops. Physical examination at birth showed a hydropic neonate with a heart rate of 70 beats/min. He had cutaneous syndactyly between the fourth and fifth fingers of the left hand. During the first week of life he suffered from polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias for which β- blocker treatment was started and an epicardial pacemaker (VVI) was implanted. An ECG a few weeks later is shown in the figure.
What is your diagnosis?
Answer
The 12-lead ECG shows sinus rhythm with a frequency of 98 beats/min. The PQ interval is 140 msec and the QRS width 60 msec (normal value for a neonate). The vertical axis is normal for the age. Repolarisation is grossly abnormal and clearly alternates in morphology every other beat. This T-wave alternans is visible in every lead but most clearly in lead V4. The QTc interval is severely prolonged and varies between 665 and 689 msec. The P wave fuses with the terminal part of the T wave and intermittently was not conducted (i.e. functional 2:1 block, not shown).
The combination severe QT-interval prolongation and syndactyly is classical for type 8 LQTS also referred to as Timothy syndrome.[1] It presents frequently at birth with life-threatening polymorphic arrhythmias in the setting of severe QTc prolongation. Besides syndactyly (present in virtually all cases) extra cardiac features include congenital defects (ASD, VSD), hypoglycaemia, and autism. In 20% a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is shown, as was also seen in our case on echocardiography. 2 Left ventricular systolic function was decreased (left ventricular shortening fraction 20%). DNA analysis in our case also revealed the de novo CaV1.2 missense mutation G406R.[1][2]
Postnatal course
After one month, he developed recurrent torsades de pointes and syncope. Mexiletine 15 mg/kg and oral potassium supplementation were added to the therapy and an extracardiac single-chamber implantable cardioverter- defibrillator (ICD) was inserted at 4 months of age. He received numerous ICD shocks and eventually died at the age of two years after cervical sympathectomy.
References
- Splawski I, Timothy KW, Sharpe LM, Decher N, Kumar P, Bloise R, Napolitano C, Schwartz PJ, Joseph RM, Condouris K, Tager-Flusberg H, Priori SG, Sanguinetti MC, and Keating MT. Ca(V)1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell. 2004 Oct 1;119(1):19-31. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.011 |
- Lo-A-Njoe SM, Wilde AA, van Erven L, and Blom NA. Syndactyly and long QT syndrome (CaV1.2 missense mutation G406R) is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2005 Dec;2(12):1365-8. DOI:10.1016/j.hrthm.2005.08.024 |