Electrolyte Disorders: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Hypercalcemia== | ==Hypercalcemia== | ||
Hypercalcemia results in a faster repolarization. Characteristics of hypercalcemia: | Hypercalcemia results in a faster repolarization. Characteristics of hypercalcemia: | ||
* | *Mild: broad based tall peaking T waves | ||
* | *Severe: extremely wide QRS, low R wave, disappearance of p waves, tall peaking T waves. | ||
==Hypocalcemia== | ==Hypocalcemia== | ||
ECG-characteristics of hypocalcemia: | ECG-characteristics of hypocalcemia: | ||
* | *Narrowing of the QRS complex | ||
* | *Reduced PR interval | ||
*T wave flattening and inversion | *T wave flattening and inversion | ||
* | *Prolongation of the QT-interval | ||
* | *Prominent U-wave | ||
* | *Prolonged ST and ST-depression | ||
==Hyperkalemia== | ==Hyperkalemia== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Hypokalemia== | ==Hypokalemia== | ||
Hypokalemia | Hypokalemia, low blood potassium, results in: | ||
*ST depression and flattening of the T wave | *ST depression and flattening of the T wave | ||
*Negative T waves | *Negative T waves | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 22 January 2010
| Author(s) | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Moderator | T.T. Keller | |
| Supervisor | ||
| some notes about authorship | ||
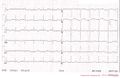
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia results in a faster repolarization. Characteristics of hypercalcemia:
- Mild: broad based tall peaking T waves
- Severe: extremely wide QRS, low R wave, disappearance of p waves, tall peaking T waves.
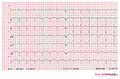
Hypocalcemia
ECG-characteristics of hypocalcemia:
- Narrowing of the QRS complex
- Reduced PR interval
- T wave flattening and inversion
- Prolongation of the QT-interval
- Prominent U-wave
- Prolonged ST and ST-depression
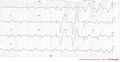
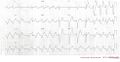
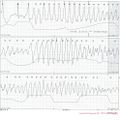
Hyperkalemia
ECG characteristics of hyperkalemia:
- Tall peaked T waves
- Flattening p-waves. In extreme hyperkalemia p-waves may disappear altogether.
- Prolonged depolarization leading to QRS widening (nonspecific intraventricular conduction defect) sometimes > 0.20 seconds
At concentrations > 7.5 mmol/L atrial and ventricular fibrillation can occur.
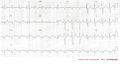
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia, low blood potassium, results in:
- ST depression and flattening of the T wave
- Negative T waves
- A U-wave may be visible